E-cigarettes first rose in popularity as a means of kicking the tobacco habit, and they were originally thought to offer a healthier way to feed the addiction to nicotine. In just a few years, smoking e-cigarettes, or vaping as it’s more commonly known, has grown to become a fad of its own. While adults do use these products, vaping has become especially popular among teens, raising concerns with parents who doubt these products are as harmless as they seem. Now, new studies are finding that e-cigarettes risks include stroke, heart attack and cancer. These findings are urging many to kick the vaping habit.
How is Vaping Different Than Smoking Cigarettes?
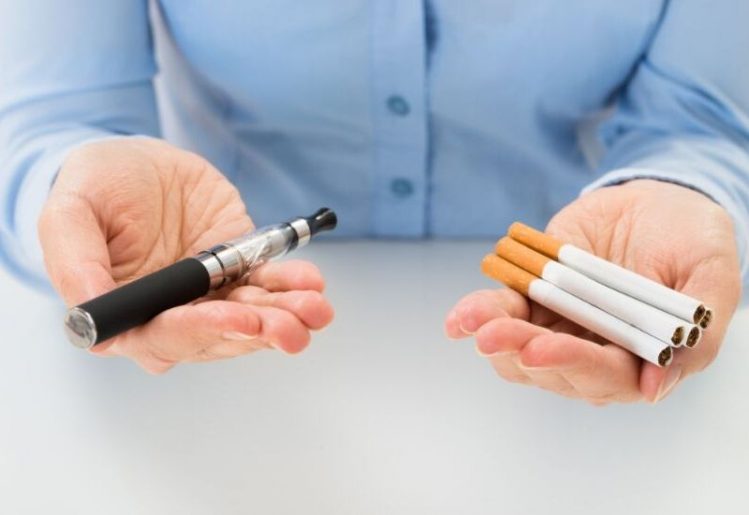 Vaping may seem to be a harmless way to obtain nicotine because there is no tobacco involved in the use of an e-cigarette. Instead, the electronic device heats a liquid product which is treated to possess distinct scents and flavors. There are a few different types of electronic devices on the market now, which include e-cigarettes and vaping pens. While the devices differ in appearance, they essentially operate in the same way. A battery inside the device heats up the e-liquid, also known as e-juice, until it becomes a vapor that the user can inhale.
Vaping may seem to be a harmless way to obtain nicotine because there is no tobacco involved in the use of an e-cigarette. Instead, the electronic device heats a liquid product which is treated to possess distinct scents and flavors. There are a few different types of electronic devices on the market now, which include e-cigarettes and vaping pens. While the devices differ in appearance, they essentially operate in the same way. A battery inside the device heats up the e-liquid, also known as e-juice, until it becomes a vapor that the user can inhale.
It was previously believed that e-juice was nothing more than flavored water vapor, but studies of the devices have found this isn’t the case. The heating process actually creates an aerosol mist that the user inhales. While an e-liquid doesn’t contain tobacco, it does contain nicotine and other additives. Various chemicals and metals, including propylene glycol, are added to the liquid. In some cases, vegetable glycerin takes the place of the propylene glycol. Much like cigarette smoke, this aerosol mist and the chemical compounds it contains is inhaled into the lungs and then exhaled.
New Research Uncovers the True Extent of E-Cigarettes Risks
In 2016, Dr. Paul Ndunda led a cross-sectional study of 400,000 subjects to determine the long-term effects of vaping. The study examined the health risks people who smoke e-cigarettes face in comparison to the health risks for those who do not smoke. They found that vaping does increase the risks of several health conditions. Specifically, the researchers found that vaping increases the risk of stroke by 71 percent. There’s also 59 percent greater risk of suffering a heart attack, or of developing angina. In general, people who use e-cigarettes and vaping pens have a 40 percent higher chance of developing heart disease.
The heart wasn’t the only organ negatively impacted by vaping. The researchers found that vaping also increased the likelihood of developing popcorn lung, or bronchiolitis obliterans (BO). It does this by creating inflammation in the airways of the lungs, which leads to scarring in these tiny airways. As a result, the individual is likely to experience shortness of breath, coughing and wheezing. This condition can sometimes be mistaken with COPD (chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), because the symptoms are very similar.
The culprit in e-cigarette mist is a chemical called diacetyl. It has long been known that diacetyl causes bronchiolitis obliterans. The chemical was formerly used in popcorn factories to give popcorn its buttery flavor, but upon discovering the health hazards this compound caused, its use was discontinued. Unfortunately, the FDA doesn’t hold e-liquid manufacturers to the same standards as food manufacturers, so it’s more difficult to determine exactly what chemicals are in the e-liquids.
A recent 2019 study examining e-cigarettes risks also found that vaping increases the risk of cancer. In fact, since e-liquids contain many of the same carcinogens as tobacco cigarettes, they may be almost as likely to cause cancer. When examining the genetic changes that occur to cause smoking-related cancer, the researchers found that those same alterations are caused by vaping. What’s more, the study found that the cancer-causing changes that are produced by vaping are more likely to occur in teens, because their bodies aren’t as fully developed.
How You Can Maintain a Healthy Heart
Quit Smoking and Vaping
 The single most important thing you can do for your heart health and cardiovascular system and to avoid e-cigarettes risks is to quit vaping and smoking. Both activities deliver harmful toxins into your blood supply, while also exposing you to the harmful effects of nicotine.
The single most important thing you can do for your heart health and cardiovascular system and to avoid e-cigarettes risks is to quit vaping and smoking. Both activities deliver harmful toxins into your blood supply, while also exposing you to the harmful effects of nicotine.
Get More Exercise
This is especially important if you have significant belly fat, since more fat accumulation in this area has been linked to hypertension and abnormal levels of blood lipids. At a minimum, you should be getting 30 minutes of moderate- to high-intensity exercise each day.
Take a Dietary Supplement
Even if you think otherwise, you’re probably not getting all of the vitamins and nutrients your body needs to stay healthy. Taking a high-quality supplement that provides the natural ingredients necessary to keep your heart healthy and strong can help maintain cardiovascular health.
Eat a Balanced, Plant-Based Diet
While you can still eat a portion of lean red meat with each meal, the bulk of your meals should be made up of fruits, vegetables, seeds, nuts and legumes. Additionally, switch to whole grains for better overall health.
Avoid Processed Foods
Pre-packaged food should be avoided as much as possible. These processed foods often contain high levels of refined sugar and trans fats, which will affect blood flow and cause weight gain.
Take Up a Hobby
Whether you enjoy building plastic models, knitting or doing crossword puzzles, it’s important to find hobbies that relax you. As you engage in stress-relieving activities, you’ll reduce the levels of stress hormones in your blood and this will help alleviate inflammation. Lowering inflammation means the heart won’t have to work as hard to efficiently pump blood throughout your body.
 The
The  In a recent study, researchers evaluated the heart health benefits of
In a recent study, researchers evaluated the heart health benefits of  Numerous studies have presented strong evidence that getting proper levels of certain crucial vitamins can help lower the risk of major chronic disease that comes with age. This research suggests that many health problems could be avoided by simply increasing the amount of vitamins we ingest on a daily basis.
Numerous studies have presented strong evidence that getting proper levels of certain crucial vitamins can help lower the risk of major chronic disease that comes with age. This research suggests that many health problems could be avoided by simply increasing the amount of vitamins we ingest on a daily basis. As people age, one of the biggest problems they face is decreased mobility, defined as the ability to move around independently. It has been determined that 30 percent of seniors do experience mobility problems. Mobility is often inhibited by long-term health conditions, such as lung disease, heart disease and arthritis. At the same time, with age, muscles, bones and tissue deteriorate, inhibiting mobility. Now, recent research into the link between vitamins and aging may have found a solution: A new study suggests an increased intake of vitamin K, commonly found in leafy green vegetables, may help boost mobility in seniors.
As people age, one of the biggest problems they face is decreased mobility, defined as the ability to move around independently. It has been determined that 30 percent of seniors do experience mobility problems. Mobility is often inhibited by long-term health conditions, such as lung disease, heart disease and arthritis. At the same time, with age, muscles, bones and tissue deteriorate, inhibiting mobility. Now, recent research into the link between vitamins and aging may have found a solution: A new study suggests an increased intake of vitamin K, commonly found in leafy green vegetables, may help boost mobility in seniors. A joint project, which brought together researchers from the U.K.’s University of East Anglia and Harvard University, looked at how eating blueberries affected the development of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. The research was intended to identify how blueberry consumption affected metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a term used to describe a situation in which an individual suffers from high blood pressure, obesity and high blood sugar. Heightened triglyceride and cholesterol levels are also common in people suffering from metabolic syndrome. When these conditions are present for an extended period of time, the individual develops increased
A joint project, which brought together researchers from the U.K.’s University of East Anglia and Harvard University, looked at how eating blueberries affected the development of heart disease and type 2 diabetes. The research was intended to identify how blueberry consumption affected metabolic syndrome. Metabolic syndrome is a term used to describe a situation in which an individual suffers from high blood pressure, obesity and high blood sugar. Heightened triglyceride and cholesterol levels are also common in people suffering from metabolic syndrome. When these conditions are present for an extended period of time, the individual develops increased 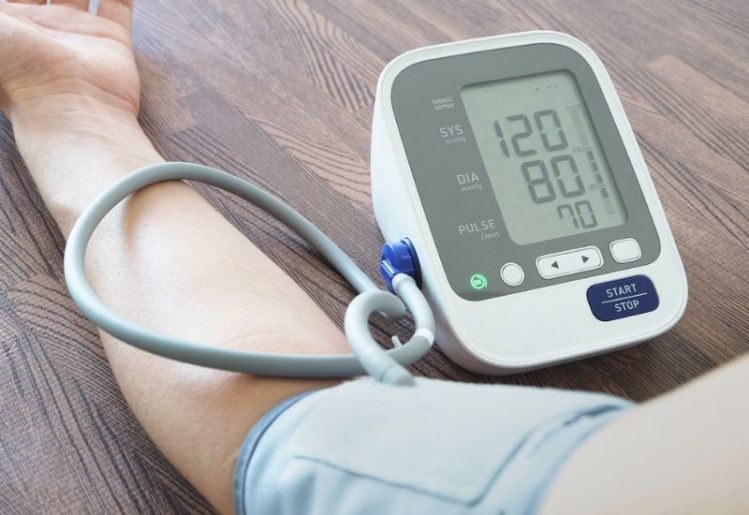 In a separate experiment, rats were given proportionate doses of anthocyanin. One of the compounds produced was vanillic acid, which was found to lower blood pressure. This may indicate that blueberries can be effective in helping patients treat hypertension, though more research is needed.
In a separate experiment, rats were given proportionate doses of anthocyanin. One of the compounds produced was vanillic acid, which was found to lower blood pressure. This may indicate that blueberries can be effective in helping patients treat hypertension, though more research is needed.
 The Tulane researchers examined the health records for their subjects at the beginning of the study and at a seven-year follow-up. The follow-up portion of the study also examined the death records for any subjects who had passed away within that time frame. In examining the records, they looked at any incidences of cardiovascular issues, which may have resulted in coronary heart disease or stroke. They also looked for any indications that death resulted from cardiovascular disease.
The Tulane researchers examined the health records for their subjects at the beginning of the study and at a seven-year follow-up. The follow-up portion of the study also examined the death records for any subjects who had passed away within that time frame. In examining the records, they looked at any incidences of cardiovascular issues, which may have resulted in coronary heart disease or stroke. They also looked for any indications that death resulted from cardiovascular disease. Much previous research has suggested that resveratrol is beneficial to heart health. A new study led by Joseph Burgoyne, Ph.D. and conducted at King’s College London sought to identify its precise
Much previous research has suggested that resveratrol is beneficial to heart health. A new study led by Joseph Burgoyne, Ph.D. and conducted at King’s College London sought to identify its precise  The study, which was conducted at Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute, sought to understand how
The study, which was conducted at Virginia Tech Carilion Research Institute, sought to understand how