The prostate gland is a small organ that’s similar in size and shape to a walnut. It’s linked to the sexual health of men in that it’s responsible for producing seminal fluid, which helps carry sperm to the penis. The prostate gland is a common target for cancer in men, but, because it develops slowly, prostate cancer may not produce observable symptoms right away. There are a number of known risk factors for prostate cancer, as well as natural ways to help protect against this common condition. Now, recent research has discovered that the health of the gut microbiome influences prostate cancer, suggesting a more diverse microbiome can help lower cancer risks.
What is Prostate Cancer?
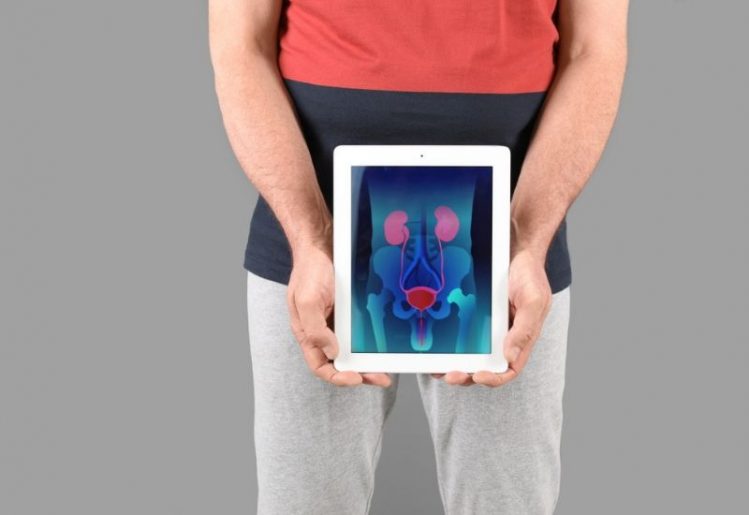 Prostate cancer is a cancer that occurs in the prostate gland, and is one of the most common types of cancer to affect men. In many cases, the cancer may stay confined to the prostate gland and may not grow large enough to pose health risks. In other cases, it may grow and spread to other parts of the body. For this reason, it’s better to diagnose prostate cancer as early as possible, so it can be treated before it has a chance to spread.
Prostate cancer is a cancer that occurs in the prostate gland, and is one of the most common types of cancer to affect men. In many cases, the cancer may stay confined to the prostate gland and may not grow large enough to pose health risks. In other cases, it may grow and spread to other parts of the body. For this reason, it’s better to diagnose prostate cancer as early as possible, so it can be treated before it has a chance to spread.
Some of the most common symptoms of prostate cancer include:
- decreased need to urinate
- less powerful urine stream
- semen that’s mixed with blood
- soreness or discomfort in the pelvic area
- bone pain
- trouble achieving or maintaining an erection
Prostate Cancer Risk Factors and Treatment
The underlying cause of prostate cancer is still unknown, but as with other cancers, it begins with the growth of abnormal or mutated cells. As the number of abnormal cells begins to outgrow the number of healthy cells, they gather together to form a tumor. As the tumor grows, it may grow large enough to pierce the tissue of the gland and spread to the rest of the body. Alternatively, some of the mutated cells can break away and travel to other parts of the body, in a process known as metastasis.
While we don’t know what causes prostate cancer to develop, the following risk factors can determine how likely an individual is of contracting the illness:
- Age: Older men are at a greater risk.
- Ethnicity: Black men face higher risks.
- Family History: If there is a history of prostate cancer or breast cancer in your family, your risk is greater.
- Obesity: Obese men face a greater risk that prostate cancer will spread or metastasize.
Prostate cancer can be treated in a number of ways. If it has remained confined to the prostate gland, the best option may be simply to remove the gland altogether. Alternatively, radiation therapy may help eradicate the cancer while leaving the gland intact. Hormone therapy is a relatively newer option, which involves depriving the cancer of the testosterone that it needs to thrive and grow. Hormone blockers stop the supply of testosterone and, as a result, the cancer weakens and dies off. The treatments your doctor recommends will depend on the severity and nature of the cancer.
New Study Finds Health of Gut Microbiome Influences Prostate Cancer
In a recent study, researchers hoped to understand how the gut microbiome influences prostate cancer, particularly in the way certain bacteria affect inflammation and infection in the prostate gland. They found that the best way to determine these bacterial influences was to examine the seminal fluid of healthy men, as well as those who had been diagnosed with prostate cancer. Additionally, prostatic fluid samples were taken from each subject. Prostatic fluid is an alkaline-based fluid that makes up part of the seminal fluid. Once the samples were taken, each of the men also submitted to a tissue biopsy. Of the 59 subjects recruited for the study, 32 of the men had been diagnosed with prostate cancer. This left them with 27 men with healthy prostate glands.
When tested, it was found that all of the men possessed high levels of prostate specific antigen (PSA). This is an enzyme secreted by the prostate gland and it’s commonly found to exist in higher levels in men with prostate cancer. However, PSA count alone isn’t enough to diagnose someone with prostate cancer, because PSA levels may be higher for any number of reasons.
After all of the samples were analyzed, the researchers found that the men with prostate cancer exhibited less bacterial diversity than those subjects with healthier prostate glands. The researchers said the findings led them to believe that a more diverse microbiome could help limit the advancement of prostate cancer.
While they admit more research is needed, they say the study does show a link between a diverse gut microbiome and a healthy prostate gland. In particular, they found that the presence of certain types of bacteria (Carnobacterium, Enterobacter, Geobacillus, Lactococcus, and Streptococcus) could affect how prostate cancer developed and grew. In the future, a test for these types of bacteria might be able to identify men who are at a greater risk of developing prostate cancer.
Natural Ways to Promote a Diverse Gut Microbiome
If you’re concerned that your gut microbiome isn’t as diverse as it should be, a few lifestyle changes may help. Below, there are listed a few tips that can help you naturally improve the diversity of your microbiome.
Eat a Diverse, Plant-Based Diet
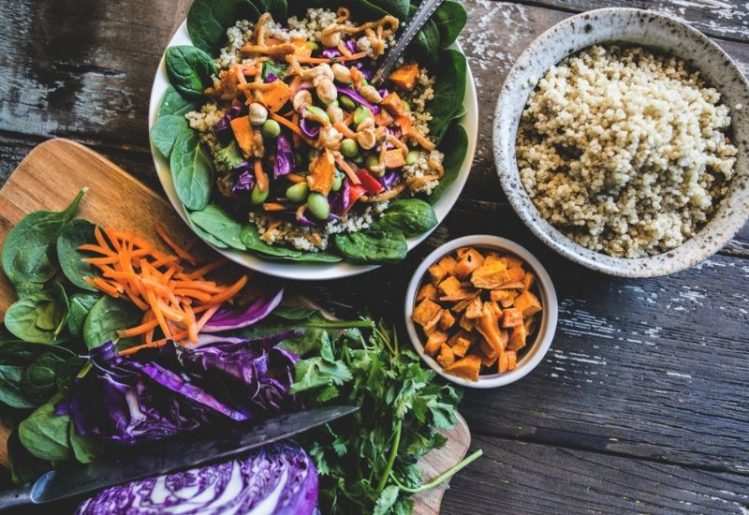 The foods you eat play a major role in building a diverse gut microbiome, but only if you’re eating healthy, natural foods. You can start by reducing your intake of sugar and trans-fats, but also strive to consume a wide selection of fruits, vegetables, seeds and nuts.
The foods you eat play a major role in building a diverse gut microbiome, but only if you’re eating healthy, natural foods. You can start by reducing your intake of sugar and trans-fats, but also strive to consume a wide selection of fruits, vegetables, seeds and nuts.
Eat Fermented Products
Foods that are fermented, such as yogurt and sauerkraut, possess a wider range of bacteria. By eating more of these foods, you can introduce a much more diverse range of bacteria into your microbiome.
Take a Dietary Supplement
You may have heard about probiotics and prebiotics, especially if you’re concerned about your physical fitness and digestive health. While probiotics can be found in certain foods, there are also supplements on the market that can help you increase the amounts of probiotics you introduce into your system. Taking a high-quality protiotic/prebiotic supplement can help you build up a diverse microbiome.
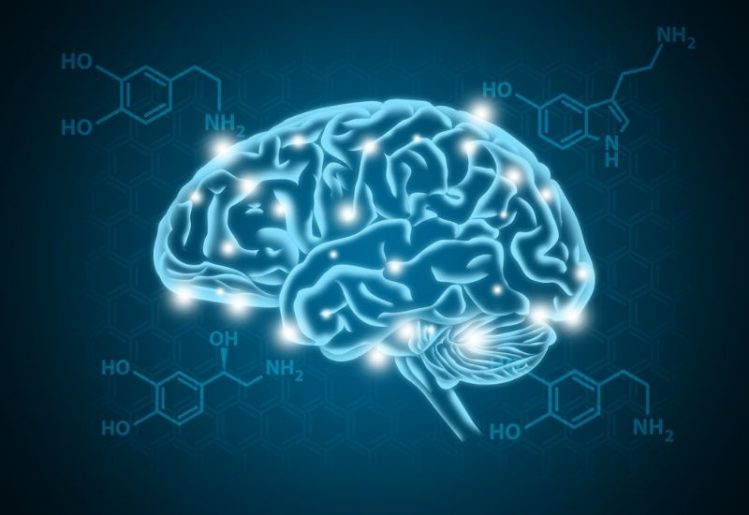 Serotonin is a well-known hormone that has become famous for its role in happiness and feelings of well-being. Scientifically known as 5-HT, this biochemical also has
Serotonin is a well-known hormone that has become famous for its role in happiness and feelings of well-being. Scientifically known as 5-HT, this biochemical also has  If a deficiency of serotonin is the cause of certain types of pain, then supplementing this hormone appears to be an easy answer. However, serotonin has special qualities that make effective supplementation a challenge. Serotonin is a large molecule that cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, which means that it can be difficult to increase levels of this hormone in the area where it matters most. Several studies suggest that a common antidepressant medication class called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or SSRIs, may help with pain by reducing the breakdown of this hormone. However, these drugs can have side effects and interactions that are a significant drawback.
If a deficiency of serotonin is the cause of certain types of pain, then supplementing this hormone appears to be an easy answer. However, serotonin has special qualities that make effective supplementation a challenge. Serotonin is a large molecule that cannot cross the blood-brain barrier, which means that it can be difficult to increase levels of this hormone in the area where it matters most. Several studies suggest that a common antidepressant medication class called selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, or SSRIs, may help with pain by reducing the breakdown of this hormone. However, these drugs can have side effects and interactions that are a significant drawback. Recently, a group of researchers analyzing records from a past Harvard University health study concluded that fruits and veggies reduce death risk from heart disease. These researchers estimate that by eating five or more servings of fruits and vegetables on a daily basis, the risk of developing heart disease may be decreased by up to 20 percent. Surprisingly, eating as much as three servings of fruits and veggies daily did not produce these same health benefits.
Recently, a group of researchers analyzing records from a past Harvard University health study concluded that fruits and veggies reduce death risk from heart disease. These researchers estimate that by eating five or more servings of fruits and vegetables on a daily basis, the risk of developing heart disease may be decreased by up to 20 percent. Surprisingly, eating as much as three servings of fruits and veggies daily did not produce these same health benefits. Currently, there is only limited research looking into the effects of eating fresh fruits on the development and treatment of diabetes. We already know that drinking fruit juice, which has high amounts of added sugar, is hazardous to those with diabetes and those at risk of developing the disease. However, some new research has found that eating fresh fruit, such as apples, blueberries and grapes, actually lowers the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. While fruit juices and fruits preserved in cans are likely to raise the risks of developing diabetes, eating leafy green vegetables and fresh fruit seems to lower those risks for both men and women.
Currently, there is only limited research looking into the effects of eating fresh fruits on the development and treatment of diabetes. We already know that drinking fruit juice, which has high amounts of added sugar, is hazardous to those with diabetes and those at risk of developing the disease. However, some new research has found that eating fresh fruit, such as apples, blueberries and grapes, actually lowers the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. While fruit juices and fruits preserved in cans are likely to raise the risks of developing diabetes, eating leafy green vegetables and fresh fruit seems to lower those risks for both men and women. While there’s much research to suggest that omega-3 fatty acids benefit heart health, a recent study looked at the benefits that another fatty acid, omega-6. This new study, led by Professor Dipak Ramji of Cardiff University, sought to determine how
While there’s much research to suggest that omega-3 fatty acids benefit heart health, a recent study looked at the benefits that another fatty acid, omega-6. This new study, led by Professor Dipak Ramji of Cardiff University, sought to determine how  In a recent observational study that involved reviewing 22 previous studies, a link was found between GLA and rheumatoid arthritis. The GLA was delivered by an increased consumption of evening primrose oil and fish oil. As a result, inflammation and pain was reduced, while subjects reported increased mobility.
In a recent observational study that involved reviewing 22 previous studies, a link was found between GLA and rheumatoid arthritis. The GLA was delivered by an increased consumption of evening primrose oil and fish oil. As a result, inflammation and pain was reduced, while subjects reported increased mobility. Research conducted recently at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine sought to confirm the theory that Parkinson’s disease first
Research conducted recently at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine sought to confirm the theory that Parkinson’s disease first  A healthy and diverse gut microbiome is more efficient at digesting your food and flushing waste out of your system. However, when there’s a problem, you’ll experience frequent stomach aches, diarrhea or constipation, heartburn and more frequent gas.
A healthy and diverse gut microbiome is more efficient at digesting your food and flushing waste out of your system. However, when there’s a problem, you’ll experience frequent stomach aches, diarrhea or constipation, heartburn and more frequent gas.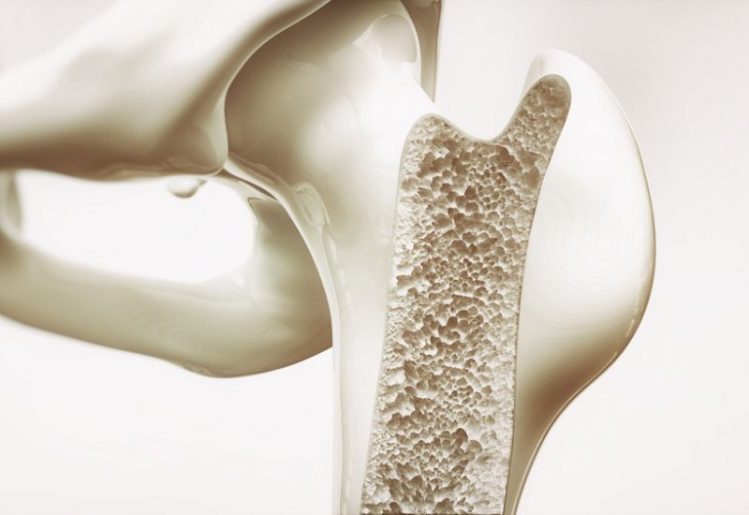 When a person develops osteoporosis, the health of their existing bones also becomes compromised. Since bone density is lost, the bones can become fragile and brittle. This is why people with osteoporosis are at a greater risk for fractures in the hips, spine and wrists. Although there are no observable symptoms of the condition, those who develop osteoporosis may exhibit a stooping of the spine. They may also experience bone pain as the condition worsens.
When a person develops osteoporosis, the health of their existing bones also becomes compromised. Since bone density is lost, the bones can become fragile and brittle. This is why people with osteoporosis are at a greater risk for fractures in the hips, spine and wrists. Although there are no observable symptoms of the condition, those who develop osteoporosis may exhibit a stooping of the spine. They may also experience bone pain as the condition worsens. If you remember the milk commercials from your childhood, you already know that calcium is essential to bone health and growth. Every adult should be consuming 1,000 mg of calcium daily, but women over 51 years should be getting 1,200 mg daily. Anyone over the age of 71 should also be getting a minimum of 1,200 mg of calcium a day. Your body
If you remember the milk commercials from your childhood, you already know that calcium is essential to bone health and growth. Every adult should be consuming 1,000 mg of calcium daily, but women over 51 years should be getting 1,200 mg daily. Anyone over the age of 71 should also be getting a minimum of 1,200 mg of calcium a day. Your body