Consuming large quantities of red meat has long been thought to have a negative impact on heart health. In the past, it was assumed this correlation was due to higher levels of saturated fats or cholesterol present in red meat, as opposed to other meats like chicken or fish. Now, a new study reveals that red meat boosts heart disease risk via its influence on gut bacteria.
New Research Confirms Red Meat Boosts Heart Disease Risk
 A recent study confirms that where people get their protein may affect their risk for heart disease. Specifically, the researchers found that diets rich in red meat raised levels of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a substance produced by gut bacteria, by more than three times when compared to people who derived their protein from white meat and other sources. The higher level of the TMAO compound is alarming because earlier research has found that high levels of TMAO can be unhealthy, particularly in relation to heart health. Specifically, TMAO encourages plaque to develop in the arteries, which affects blood flow and the heart’s ability to circulate blood.
A recent study confirms that where people get their protein may affect their risk for heart disease. Specifically, the researchers found that diets rich in red meat raised levels of trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO), a substance produced by gut bacteria, by more than three times when compared to people who derived their protein from white meat and other sources. The higher level of the TMAO compound is alarming because earlier research has found that high levels of TMAO can be unhealthy, particularly in relation to heart health. Specifically, TMAO encourages plaque to develop in the arteries, which affects blood flow and the heart’s ability to circulate blood.
This study, conducted at Ohio’s Cleveland Clinic, found that red meat influenced the production of TMAO in a couple of ways. As gut bacteria produce high levels of TMAO, that compound changes platelets in the blood and promotes a higher risk of blood clot formation. It does this by increasing the level of calcium in the platelets, which influences how those platelets respond to the body’s indicators that blood clotting is needed. This means dangerous clots can form in the blood even if the blood pressure and cholesterol levels are at healthy levels.
This new research has been supported by other studies as well. A study at the University of Leicester revealed that people suffering from acute conditions of heart failure responded less successfully to treatment if they had high TMAO levels. Under these circumstances, incidences of heart attack and stroke resulted in death more often than in patients with lower levels of TMAO.
Protein Choices Can Affect Heart Health
In the most recent study, which was engineered to examine how red meat boosts heart disease risk, 113 participants were divided into three groups. Following a general detox diet that helped flush toxins out of the body, each group was assigned a different diet. Each diet was planned according to varying sources of protein.
One group was assigned a diet that derived 12 percent of its calories from beef, pork and other types of lean red meat. The second group obtained protein from a comparable portion size of white meat, such as poultry. In the third group, participants consumed 12 percent of their calorie intake from non-meat protein sources. These consisted of legumes, nuts, whole grains and soy products. An additional 13 percent of calorie intake consisted of proteins derived from dairy products and vegetables for all three groups.
Four weeks into the study, individuals on the red meat plan had notable increases of TMAO in their blood and urine samples. On average, TMAO levels tripled for the red meat eaters, but, in some cases, the level of TMAO was up to ten times higher.
The study also yielded an unexpected finding. Throughout the study, participants on the red meat diet exhibited inhibited kidney function. The higher levels of TMAO weren’t processed as efficiently by the kidneys, though the high levels of the compound did dissipate after the participants were instructed to resume a healthier diet. While this indicates that red meat does affect our heart health via the production of trimethylamine N-oxide, the research also suggests that risk can be reduced by simple dietary changes. The research also indicates that diets consisting of white meat and non-meat protein sources are healthier for the heart.
More Ways to Boost Heart Health
While eliminating red meat from your diet is an excellent way to improve heart health, it’s not the only dietary change you can make. The following foods and beverages also improve heart health in different ways. By adding some of these items to your daily diet, you can improve your overall health.
Green Tea
Most people already know that green tea is packed with several antioxidants. These compounds help lower blood pressure and reduce the levels of LDL cholesterol in the body. Green tea can be enjoyed warm or cold.
Olive Oil
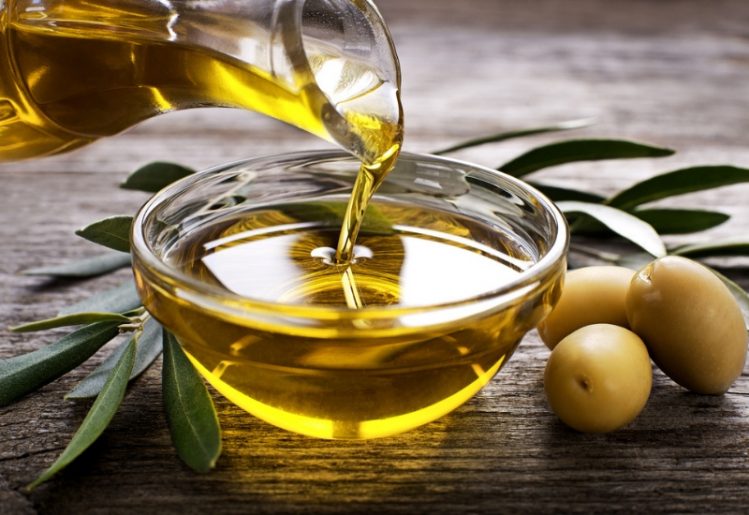 Ditch the vegetable and canola oils that you usually cook with and replace them with olive oil. This natural oil is rich in monounsaturated fatty acid, which affects cholesterol in two ways: While it reduces the level of LDL cholesterol, it also increases the level of HDL or good cholesterol in the body. Olive oil is also rich in disease-fighting antioxidants.
Ditch the vegetable and canola oils that you usually cook with and replace them with olive oil. This natural oil is rich in monounsaturated fatty acid, which affects cholesterol in two ways: While it reduces the level of LDL cholesterol, it also increases the level of HDL or good cholesterol in the body. Olive oil is also rich in disease-fighting antioxidants.
Fiber
People who eat high amounts of fiber are less likely to experience heart attacks. You can get the fiber you need from whole grain breads and cereals, wheat bran, oats, and beans. Typically, you should be eating between 25 to 35 grams of fiber each day.
Fish
As long as you’re trying to eliminate red meat from your diet, why not replace it with salmon, tuna or anchovies. These fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which boosts heart health. Some research indicates that just one serving of fish per week reduces your risk of a heart attack by 52 percent or more.
In addition to controlling what foods you eat, your daily activities have an effect on your heart health. Getting daily physical activity and ensuring you’re getting enough quality sleep are more ways to promote better heart health. Additionally, if you are concerned about the condition of your heart, discussing your concerns with your doctor can also help.
 Although most people have gotten the flu and recovered, it is actually one of the greatest disease threats of our time. Before knowledge about sanitation and widespread vaccination made flu less common, millions of people would die from this disease in just one flu season. Even in modern times, the flu is a very real risk to children, the elderly and people with compromised immune systems. In addition, it can cause a week or more of high fever and other serious symptoms even in the healthiest among us.
Although most people have gotten the flu and recovered, it is actually one of the greatest disease threats of our time. Before knowledge about sanitation and widespread vaccination made flu less common, millions of people would die from this disease in just one flu season. Even in modern times, the flu is a very real risk to children, the elderly and people with compromised immune systems. In addition, it can cause a week or more of high fever and other serious symptoms even in the healthiest among us.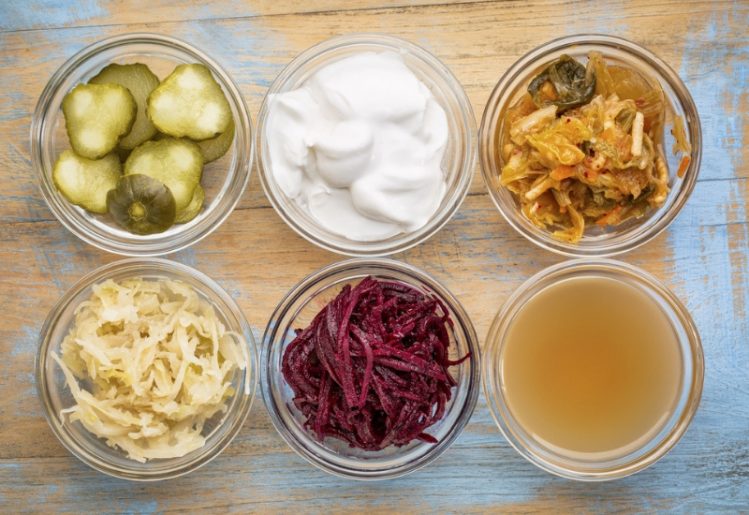 Hippocrates, father of modern medicine and writer of the famous Hippocratic oath, once noted, “Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food.” However, the modern Western diet does more to harm our microflora than to help it. We eat meat that has been fed antibiotics, which we then absorb. We clean our houses from top to bottom with antimicrobial cleansers. Americans also do not ingest adequate amounts of traditional fermented foods, which are teeming with healthy probiotic organisms.
Hippocrates, father of modern medicine and writer of the famous Hippocratic oath, once noted, “Let food be thy medicine and medicine be thy food.” However, the modern Western diet does more to harm our microflora than to help it. We eat meat that has been fed antibiotics, which we then absorb. We clean our houses from top to bottom with antimicrobial cleansers. Americans also do not ingest adequate amounts of traditional fermented foods, which are teeming with healthy probiotic organisms. Depression and anxiety are growing problems in the modern world. Depression, which is defined as a low mood along with fatigue, inability to enjoy normally enjoyable activities and physical symptoms such as pain and loss of appetite,
Depression and anxiety are growing problems in the modern world. Depression, which is defined as a low mood along with fatigue, inability to enjoy normally enjoyable activities and physical symptoms such as pain and loss of appetite,  There are several natural remedies that have been found in clinical trials to positively affect mood and treat many of the unwanted symptoms of depression and anxiety.
There are several natural remedies that have been found in clinical trials to positively affect mood and treat many of the unwanted symptoms of depression and anxiety.  All men should be able to identify the common
All men should be able to identify the common  Regardless of how they’re prepared, tomatoes are believed to
Regardless of how they’re prepared, tomatoes are believed to  Recently, a team of University of Tasmania researchers led by Michele Callisaya conducted a study to find out why cognitive decline is prevalent in people with type 2 diabetes. The project looked at 705 adults between the ages of 55 and 90. The testing included brain size measurements as well as cognition evaluations.
Recently, a team of University of Tasmania researchers led by Michele Callisaya conducted a study to find out why cognitive decline is prevalent in people with type 2 diabetes. The project looked at 705 adults between the ages of 55 and 90. The testing included brain size measurements as well as cognition evaluations. Increasing the amount of
Increasing the amount of  A new body of research, dubbed the
A new body of research, dubbed the  While controlling obesity based on the body’s circadian rhythm may still be a few years off, you can still take action to limit or prevent gaining weight throughout this time of year. If you have your heart set on indulging in your favorite holiday foods, you might want to try
While controlling obesity based on the body’s circadian rhythm may still be a few years off, you can still take action to limit or prevent gaining weight throughout this time of year. If you have your heart set on indulging in your favorite holiday foods, you might want to try