Could mental disorders like dementia be connected to gut bacteria? This seemingly unlikely correlation may not be so far-fetched: New research suggests that an imbalance of healthy gut bacteria could be one of the possible causes of dementia, a mental condition that primarily affects the elderly.
Gut Bacteria and Dementia Defined
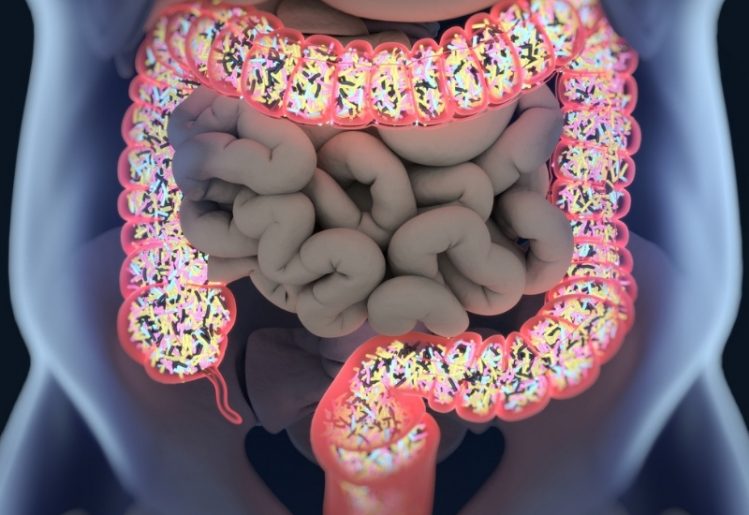 The gut’s microbiome is made up of trillions of microorganisms which include approximately a thousand diverse types of known bacteria. The human intestines are brimming with these “friendly” bacteria, and nearly a third of the various gut bacteria we each carry are also present in others. However, the remaining two-thirds are specific to each individual, meaning no two people share an entirely identical microbiome. Furthermore, humans aren’t innately born with gut bacteria — it is only acquired over time.
The gut’s microbiome is made up of trillions of microorganisms which include approximately a thousand diverse types of known bacteria. The human intestines are brimming with these “friendly” bacteria, and nearly a third of the various gut bacteria we each carry are also present in others. However, the remaining two-thirds are specific to each individual, meaning no two people share an entirely identical microbiome. Furthermore, humans aren’t innately born with gut bacteria — it is only acquired over time.
Despite the negative connotations associated with bacteria, gut microbiota aren’t all that bad. In fact, they are responsible for quite a few functions in our bodies. First off, these bacteria are crucial for the proper digestion of the food we eat. The gut microbiome also plays an important role in our immune system. Essentially, a balanced and maintained gut microbiome is necessary for optimal digestion and immune system function.
Dementia, on the other hand, isn’t exactly a disease, but it is a collection of symptoms typically experienced by the elderly. Dementia is characterized by a person’s inability to perform cognitive tasks, along with massive degradation of memory. Other common symptoms of dementia include impaired reasoning, judgment and communication skills, the inability to focus and impaired visual perception. Most of dementia’s symptoms affect the brain. Although it has been known of and researched for years, there’s a lot we’ve yet to learn about dementia, including how it actually begins.
Considering the dissimilarities between the areas affected by mental disorders like dementia and the topic of gut bacteria and digestion, it may be surprising that there is a potential link between the two.
Gut Bacteria as a Guide for the Diagnosis And Treatment Of Dementia
The naturally occurring bacteria in our body have been examined as part of a broader scope when it comes to treating diseases. With this principle in mind, Dr. Naoki Saji, along with researchers from the Center for Comprehensive Care and Research on Memory Disorders at the National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology in Obu, Japan, headed up a new study centered on gut bacteria. The group presented their findings at the American Stroke Association’s International Stroke Conference 2019 in February 2019.
To conduct the study, the researchers recruited the help of 128 patients from their own memory clinic. Of the participants, 59 percent were female and the average age was 74. The patients were assisted in completing various tests that measured cognitive ability. Furthermore, some of the participants had dementia while others did not. To shed light on the role of gut bacteria in dementia, the researchers analyzed fecal samples from the respondents.
Surprisingly, the researchers found significant differences in the bacterial populations from the subjects with dementia versus those who do not have it. The common pattern observed was that the patients with dementia had elevated levels of specific bacteria such as indole, skatole, phenol, ruminococcus and ammonia. Furthermore, the dementia patients also had lower levels of good bacteria called bacteroides.
The big takeaway from the findings is that in the future, a patient’s fecal matter may possibly be used to determine whether or not he or she has dementia. Since the bacteria count in the dementia patients was similar among participants, it could theoretically be used as a diagnostics tool in the future. Of course, this concept will need more research before being commonly utilized in a clinical setting.
Gut Bacteria Also Linked to Other Mental Conditions
 Beyond the findings from Dr. Saji and his team, researchers from the Catholic University of Leuven in Belgium have also found a link between gut bacteria composition and clinical depression. According to the researcher’s findings, published in Nature Microbiology, most of the gut bacteria in our body are able to create neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin. The researchers also figured out that people who have been diagnosed with depression lacked two specific strains of bacteria.
Beyond the findings from Dr. Saji and his team, researchers from the Catholic University of Leuven in Belgium have also found a link between gut bacteria composition and clinical depression. According to the researcher’s findings, published in Nature Microbiology, most of the gut bacteria in our body are able to create neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin. The researchers also figured out that people who have been diagnosed with depression lacked two specific strains of bacteria.
The study is still in its early stages, but considering the large amount of recent research dedicated to gut health, the new findings are sure to bolster the idea that gut bacteria have more to do than just help with the digestive process.
In a case similar to Dr. Sajia and his team’s findings, there is a chance that fecal matter and a person’s gut bacteria can be used in the future to diagnose clinical depression. If more research is conducted, there is also a chance that the findings could be turned into a possible treatment for depression.
The research from Dr. Saji and his team has the potential to change the way doctors diagnose and treat dementia. Hopefully, the team finds more success in the coming months and we will see new developments regarding this scientific breakthrough.
 Many cancer studies are geared towards finding ways to treat this devastating condition. So far, the most popular form of treatment is chemotherapy, but it has its downside in relation to its effects on the human body. Luckily, more researchers are discovering other methods that are less harmful and could even be more effective.
Many cancer studies are geared towards finding ways to treat this devastating condition. So far, the most popular form of treatment is chemotherapy, but it has its downside in relation to its effects on the human body. Luckily, more researchers are discovering other methods that are less harmful and could even be more effective. Nanotechnology is one of the emerging fields leading the charge when it comes to cancer treatment. In cancer treatment, nanotechnology is commonly used in a treatment called nanotechnology chemotherapy. There are many forms of nanotechnology treatments when it comes to fighting cancer — but according to a new study, it seems like certain nanoparticles may in fact promote cancer growth.
Nanotechnology is one of the emerging fields leading the charge when it comes to cancer treatment. In cancer treatment, nanotechnology is commonly used in a treatment called nanotechnology chemotherapy. There are many forms of nanotechnology treatments when it comes to fighting cancer — but according to a new study, it seems like certain nanoparticles may in fact promote cancer growth. Chemotherapy holds its ground as the most popular and readily available treatment for treating cancer and tumors, but it has had its criticisms throughout the years. The treatment utilizes a anti-cancer drugs in an attempt to kill off cancer cells, and while proven effective, it does take a toll on the human body and might even harm your brain.
Chemotherapy holds its ground as the most popular and readily available treatment for treating cancer and tumors, but it has had its criticisms throughout the years. The treatment utilizes a anti-cancer drugs in an attempt to kill off cancer cells, and while proven effective, it does take a toll on the human body and might even harm your brain. People who rarely engage in social interaction with others may be harming their brains as well. Failing to meet one’s physical, mental and social needs could lead to
People who rarely engage in social interaction with others may be harming their brains as well. Failing to meet one’s physical, mental and social needs could lead to  Aside from the problems caused by the over-prescription of antibiotics, recent research has uncovered other
Aside from the problems caused by the over-prescription of antibiotics, recent research has uncovered other  In recent years, the
In recent years, the  In the 20 year span from 1990 through 2010, the CDC calculated that the number of diabetics tripled. Additionally, they found that twice as many people were being diagnosed with the disease from one year to the next. While anyone can develop diabetes, the risks increase with age. The recent CDC report highlighted the percentage of people living with diabetes within each age group:
In the 20 year span from 1990 through 2010, the CDC calculated that the number of diabetics tripled. Additionally, they found that twice as many people were being diagnosed with the disease from one year to the next. While anyone can develop diabetes, the risks increase with age. The recent CDC report highlighted the percentage of people living with diabetes within each age group: The bottom line: If you really want to lower your diabetes risk, it’s necessary to make changes in your life now. While people are often born with type 1 diabetes, a condition in which your body isn’t making insulin, type 2 diabetes, a condition that involves your cells’ inability to properly process the insulin, develops over time and its development is often influenced by lifestyle choices.
The bottom line: If you really want to lower your diabetes risk, it’s necessary to make changes in your life now. While people are often born with type 1 diabetes, a condition in which your body isn’t making insulin, type 2 diabetes, a condition that involves your cells’ inability to properly process the insulin, develops over time and its development is often influenced by lifestyle choices. Most of us think nothing of reaching for their favorite syrupy medicine at the first signs of a cold or flu. Although these medications can be very effective for symptoms such as fever and cough, the American Heart Association warns that they can have
Most of us think nothing of reaching for their favorite syrupy medicine at the first signs of a cold or flu. Although these medications can be very effective for symptoms such as fever and cough, the American Heart Association warns that they can have  These factors are all surprising because they are common in our society, yet are not commonly associated with heart health. However, they are not the only things that are contributing to our steady decline in cardiovascular health. Many of the best ways to preserve your heart health are
These factors are all surprising because they are common in our society, yet are not commonly associated with heart health. However, they are not the only things that are contributing to our steady decline in cardiovascular health. Many of the best ways to preserve your heart health are