Most people are aware of the importance of getting sufficient vitamins in our daily diet, whether from foods or from supplements. However, new research suggests that it is also important to get these critical nutrients at the correct time of day. This may be particularly important with vitamin B6, a vitamin that plays a key role in energy production. Could the timing of your vitamin intake have an impact on your health and well-being? Should you be taking vitamin B6 in the morning? Read on to find out.
Vitamin B6’s Role in Energy
 Like many B vitamins, vitamin B6 is best known for its role in energy production. Also known as pyridoxine, this vitamin acts as a cofactor in several important metabolic processes. Most notably, it is crucial in creating energy for our cells. Although taking more than the daily recommended amount of vitamin B6 has not been found to increase energy per se, not having enough of this nutrient can cause fatigue as well as other unpleasant symptoms.
Like many B vitamins, vitamin B6 is best known for its role in energy production. Also known as pyridoxine, this vitamin acts as a cofactor in several important metabolic processes. Most notably, it is crucial in creating energy for our cells. Although taking more than the daily recommended amount of vitamin B6 has not been found to increase energy per se, not having enough of this nutrient can cause fatigue as well as other unpleasant symptoms.
Vitamin B6 also plays an important role in the creation of certain neurochemicals. Perhaps most significantly, it plays a critical role in the creation of serotonin from its precursor tryptophan. Even a mild deficiency of vitamin B6 can negatively affect serotonin levels, leaving us feeling fatigued and out of sorts. When serotonin levels drop, people may experience a wide variety of unpleasant effects, including changes in their circadian rhythm and mood.
Although serotonin levels are important to our health in a variety of ways, there are very few medications that work to help to keep this hormone stable. SSRIs, antidepressant drugs that increase serotonin, can cause increases in blood serotonin. However, the increase is often very small. For many people, the best way to influence serotonin levels is to take vitamin B6, tryptophan and other substances that play a part in serotonin synthesis. This naturally encourages the body to create more of this key hormone, solving the root problem without side effects or risks.
Serotonin and Sleep
Why do we need so much serotonin in the first place? Serotonin is one of the most effective multi-taskers in the human body, affecting almost every aspect of our health. Produced in the pineal gland along with melatonin and other neurochemicals, this hormone is best known for its role in creating a sense of happiness and well-being. However, it also has other important functions. For example, it has critical roles in heart health, digestion and even metabolism.
Most notably, serotonin appears to be extremely important in sleep regulation. When levels of this hormone are high, we feel energetic and alert. When they are low, we are more likely to feel sleepy. Sometimes this sleepiness is necessary and healthy, such as at night when we are trying to sleep. Serotonin does not just help us to sleep, but also promotes healthy sleep-wake cycles. Our levels are lowest when we are in REM sleep, which is the phase in which we dream.
Although higher levels of serotonin are associated with greater happiness and well-being, timing is an important factor. High levels of serotonin are most beneficial during the day, while they could actually cause insomnia if this hormone is high at night. As with all other aspects of health, timing is an important factor.
Why Take Vitamin B6 in the Morning?
 Because vitamin B6 is important to the manufacture of serotonin, it is best taken when we first awake in the morning. We sleep more soundly and dream best when our serotonin levels are low. On the other hand, we benefit from a boost of serotonin during the day. Taking B6 as well as other energy-promoting vitamins in the morning just may give you the extra energy and mood boost that you need to get the day to a pleasant and productive start.
Because vitamin B6 is important to the manufacture of serotonin, it is best taken when we first awake in the morning. We sleep more soundly and dream best when our serotonin levels are low. On the other hand, we benefit from a boost of serotonin during the day. Taking B6 as well as other energy-promoting vitamins in the morning just may give you the extra energy and mood boost that you need to get the day to a pleasant and productive start.
Although it may seem unusual that time of day matters in taking vitamins, new research in the field of chronobiology is discovering an increasing number of ways that timing can make a huge difference in health. In addition, to vitamins, several medications have been found to be more effective or have fewer side effects when taken at specific times of the day. The more we can work with our internal clocks, the better results we can expect.
Getting Your Day Off to a Great Start
Although supplementing with vitamin B6 is a great way to boost morning energy, there are several healthy and natural ways to make sure you have the get-up-and-go that you need to get up and go. Make sure you get around six to eight hours of rest every night. Go to bed and awaken at the same time every day to ensure that your circadian clocks keep ticking on time. Rather than a cup of coffee, reach for a healthy breakfast and a multivitamin with B6 as well as other vitamins that promote energy.
 Recent studies have found that the majority of individuals suffering from cardiovascular disease also suffer from depression. Since the two conditions commonly occur together, it seems very likely that there may be a
Recent studies have found that the majority of individuals suffering from cardiovascular disease also suffer from depression. Since the two conditions commonly occur together, it seems very likely that there may be a  Getting more physical exercise can help
Getting more physical exercise can help  Depression encompasses more than merely feeling down or being unhappy. This condition is a
Depression encompasses more than merely feeling down or being unhappy. This condition is a  In a second study, a group of Belgian biologists found a significant link between an individual’s
In a second study, a group of Belgian biologists found a significant link between an individual’s  The
The  Beyond the findings from Dr. Saji and his team, researchers from the Catholic University of Leuven in Belgium have also found a link between gut bacteria composition and clinical depression. According to the researcher’s findings, published in Nature Microbiology, most of the gut bacteria in our body are able to create neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin. The researchers also figured out that people who have been diagnosed with
Beyond the findings from Dr. Saji and his team, researchers from the Catholic University of Leuven in Belgium have also found a link between gut bacteria composition and clinical depression. According to the researcher’s findings, published in Nature Microbiology, most of the gut bacteria in our body are able to create neurotransmitters, including dopamine and serotonin. The researchers also figured out that people who have been diagnosed with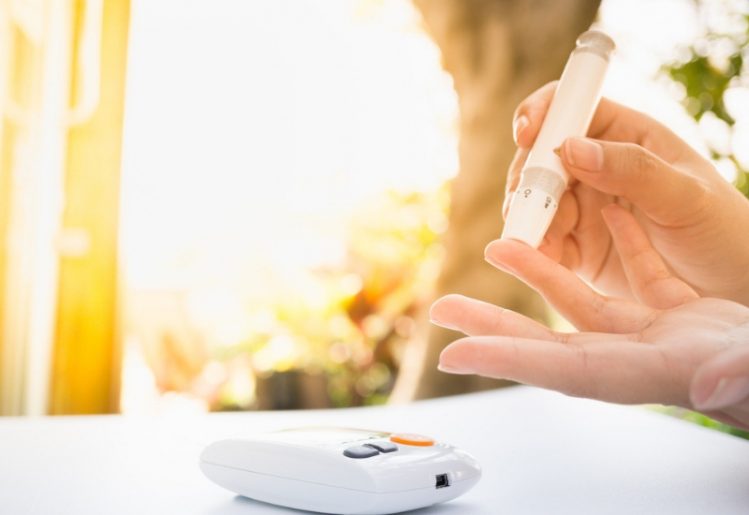  In the 20 year span from 1990 through 2010, the CDC calculated that the number of diabetics tripled. Additionally, they found that twice as many people were being diagnosed with the disease from one year to the next. While anyone can develop diabetes, the risks increase with age. The recent CDC report highlighted the percentage of people living with diabetes within each age group:
In the 20 year span from 1990 through 2010, the CDC calculated that the number of diabetics tripled. Additionally, they found that twice as many people were being diagnosed with the disease from one year to the next. While anyone can develop diabetes, the risks increase with age. The recent CDC report highlighted the percentage of people living with diabetes within each age group: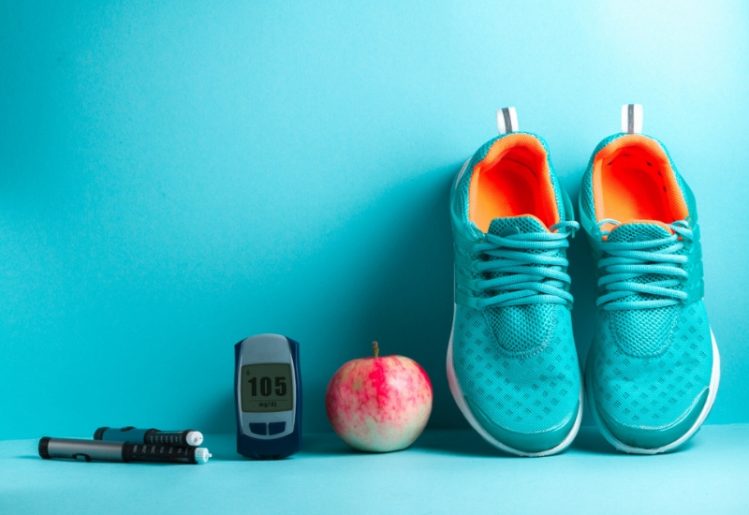 The bottom line: If you really want to lower your diabetes risk, it’s necessary to make changes in your life now. While people are often born with type 1 diabetes, a condition in which your body isn’t making insulin, type 2 diabetes, a condition that involves your cells’ inability to properly process the insulin, develops over time and its development is often influenced by lifestyle choices.
The bottom line: If you really want to lower your diabetes risk, it’s necessary to make changes in your life now. While people are often born with type 1 diabetes, a condition in which your body isn’t making insulin, type 2 diabetes, a condition that involves your cells’ inability to properly process the insulin, develops over time and its development is often influenced by lifestyle choices. Depression and anxiety are growing problems in the modern world. Depression, which is defined as a low mood along with fatigue, inability to enjoy normally enjoyable activities and physical symptoms such as pain and loss of appetite,
Depression and anxiety are growing problems in the modern world. Depression, which is defined as a low mood along with fatigue, inability to enjoy normally enjoyable activities and physical symptoms such as pain and loss of appetite,  There are several natural remedies that have been found in clinical trials to positively affect mood and treat many of the unwanted symptoms of depression and anxiety.
There are several natural remedies that have been found in clinical trials to positively affect mood and treat many of the unwanted symptoms of depression and anxiety.