Menopause is a natural occurrence in a woman’s life, and as such should not be considered an illness or adverse medical condition. Although it typically occurs when a woman reaches her 40s or 50s, it can occur earlier. The onset of menopause is marked by a woman’s last menstrual period; specifically, menopause commences with the cessation of the menstrual cycle for at least a 12-month period. While this is a natural occurrence, it does produce some adverse symptoms, which women may experience for years after they have had their last period. The severity and frequency of the symptoms will vary from woman to woman, so some may only experience them for a brief time. A new study finds that two lifestyle habits increase the chances of experiencing menopause hot flashes, offering a possible way to reduce the risk of certain menopausal symptoms.
What are Some Symptoms of Menopause?
 Once a woman experiences menopause, she’s no longer fertile and cannot conceive a child. This is just one result of the lower levels of estrogen the body now produces. Since hormone levels are decreased during this period, other physical and emotional changes can also occur. These symptoms often include:
Once a woman experiences menopause, she’s no longer fertile and cannot conceive a child. This is just one result of the lower levels of estrogen the body now produces. Since hormone levels are decreased during this period, other physical and emotional changes can also occur. These symptoms often include:
- vaginal dryness
- hot flashes
- night sweats
- irregular sleep patterns
- urinary problems, including urinary tract infection
- depression
- mood swings
- inhibited cognitive abilities, especially poor concentration and memory recall
As women enter this stage in their lives, they also have a greater risk of developing certain diseases. Lower estrogen levels raise the risks of cardiovascular disease, osteoporosis and breast cancer. In some cases, women can counteract these increased risks by altering their diets, increasing physical activity and making other natural changes.
Certain Lifestyle Habits Increase Risk of Menopause Hot Flashes
Two of the most troubling symptoms that women experience are menopause hot flashes and night sweats. According to some new research, these symptoms can be alleviated by making a few lifestyle modifications, but only if the changes are made earlier in life. The researchers found that hot flashes and night sweats were less common among women who had quit smoking and reduced their body fat by the age of 40.
It’s believed that the hypothalamus region of the brain is responsible for controlling body temperature. A misfiring in this part of the brain may be responsible for causing the hot flashes and night sweats that older women experience after menopause. These symptoms, which are called vasomotor symptoms, are experienced by more than 85 percent of menopausal women. New research that was conducted at Australia’s University of Queensland suggests vasomotor symptoms may be avoided with some lifestyle changes.
Dr. Hsin-Fang Chung led the project, which involved combing over eight previous studies that evaluated the health of 21,460 middle-aged women. The subjects in the study were all over 50 years of age and consisted of women from the U.S., U.K., Japan and Australia. The team compared obesity and smoking habits of the subjects against their risks of experiencing vasomotor symptoms. In making the comparisons, the researchers noted how the changes occurred in relation to the stage of menopause each subject was experiencing.
As the research project began, more than 60 percent of the subjects reported experiencing night sweats or hot flashes. The researchers also noted that more than half of the women in that group were overweight, with 21 percent of them registering as obese. Additionally, 17 percent were smokers. The study revealed that the women who were smokers and/or obese for most of their lives experienced vasomotor symptoms more frequently and more severely as they reached menopause.
Specifically, Dr. Chung reported that obesity raised the risks of experiencing more pronounced vasomotor symptoms by 60 percent. Smokers raised their risk of experiencing hot flashes and night sweats in menopause by 80 percent when compared to non-smoking women. When combined, smoking and obesity raises the risks of experiencing more severe hot flashes and night sweats by three times. This was found to be especially true for women who smoked more than 20 cigarettes daily, or those who had smoked for more than 30 years consistently.
The research found that these effects could be prevented by making early lifestyle changes. The women who quit smoking before the age of 40 faced the same risks of experiencing severe vasomotor symptoms as women who had never smoked. Similarly, dropping excess weight earlier in life will help women enjoy these same benefits when they do reach menopause.
How Can You Alleviate the Symptoms of Menopause Naturally?
Improve Your Diet
 Your eating habits can greatly affect the severity of your menopausal symptoms. Spicy foods should be avoided as much as possible, while coffee, soda and alcohol should be eliminated. Staying away from caffeinated products in the late afternoons and evening hours can also improve sleep quality. Your doctor can provide you with a more thorough list of foods you should avoid and those you should add to your diet.
Your eating habits can greatly affect the severity of your menopausal symptoms. Spicy foods should be avoided as much as possible, while coffee, soda and alcohol should be eliminated. Staying away from caffeinated products in the late afternoons and evening hours can also improve sleep quality. Your doctor can provide you with a more thorough list of foods you should avoid and those you should add to your diet.
Take a Supplement
A daily supplement, such as Menochron, can also help alleviate certain menopause symptoms. The supplement’s isoflavones mimic the effects that natural estrogen has on the body, supporting healthy hormone balance and helping to make up for the lower levels of hormones. Additionally, other ingredients help the body metabolize sugar and fat more efficiently, protect bone health and fight free radicals. Research also shows that testosterone supplementation may help boost libido and improve sexual health during menopause.
Get More Exercise
The body needs a minimum of 30 minutes of exercise each day, but women facing menopause should be getting more physical activity. Workouts should combine cardio activities such as brisk walking, jogging or swimming with resistance training activities like lifting weights, push-ups and crunches, and should make up at least 60 minutes of each day.
Physical Therapy May Help
Finally, yoga, acupuncture and massage therapy may help to reduce some symptoms. While these treatments haven’t been shown to affect vasomotor symptoms, they may help alleviate other symptoms. They can help keep the body more limber, so workouts will be more effective, and they reduce stress and allow subjects to rest easier. If you have difficulty sleeping, one of these methods may improve your ability to sleep soundly.
 Once the results were examined, the researchers found that those who drank larger quantities of coffee had a greater amount of the beneficial bacteria Faecalibacterium and Roseburia in their guts. The research team also found a higher presence of other beneficial bacteria. Additionally, the presence of a harmful bacteria, Erysipelatoclostridium, was found to be much lower. These results were found to be consistent regardless of age and the quality of the individual’s diet. Previously, Erysipelatoclostridium has been linked to metabolic syndrome. It boosts the levels of glucose and fat transporters in the small intestines, which increases the risk of obesity in individuals who eat poor diets.
Once the results were examined, the researchers found that those who drank larger quantities of coffee had a greater amount of the beneficial bacteria Faecalibacterium and Roseburia in their guts. The research team also found a higher presence of other beneficial bacteria. Additionally, the presence of a harmful bacteria, Erysipelatoclostridium, was found to be much lower. These results were found to be consistent regardless of age and the quality of the individual’s diet. Previously, Erysipelatoclostridium has been linked to metabolic syndrome. It boosts the levels of glucose and fat transporters in the small intestines, which increases the risk of obesity in individuals who eat poor diets. Living a stressful lifestyle has a range of adverse effects on your health. This includes disrupting the healthy functioning of the microorganisms in your gut. If you feel stressed, take time to meditate, read a book, or go for a walk.
Living a stressful lifestyle has a range of adverse effects on your health. This includes disrupting the healthy functioning of the microorganisms in your gut. If you feel stressed, take time to meditate, read a book, or go for a walk. A recent study sought to uncover how capsaicin relieves pain, particularly since this compound has become a common ingredient in many natural pain relievers. Researchers at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School found that capsaicin causes the nerves in the body to send out signals that block pain receptors. Since this process also works to calm the nerves, study author Tibor Rohacs believes capsaicin can also be used as an effective analgesic. It was found that these calming and pain-relieving effects were highly effective and very long-lasting, suggesting that capsaicin supplements and medications may be especially powerful in terms of treating pain and other conditions.
A recent study sought to uncover how capsaicin relieves pain, particularly since this compound has become a common ingredient in many natural pain relievers. Researchers at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School found that capsaicin causes the nerves in the body to send out signals that block pain receptors. Since this process also works to calm the nerves, study author Tibor Rohacs believes capsaicin can also be used as an effective analgesic. It was found that these calming and pain-relieving effects were highly effective and very long-lasting, suggesting that capsaicin supplements and medications may be especially powerful in terms of treating pain and other conditions. Finally, a study on how capsaicin affects longevity found that people who regularly consumed chili peppers were likely to live up to 18 years longer. The University of Vermont study evaluated the effects of consuming chili peppers on 16,000 subjects. They found that the food
Finally, a study on how capsaicin affects longevity found that people who regularly consumed chili peppers were likely to live up to 18 years longer. The University of Vermont study evaluated the effects of consuming chili peppers on 16,000 subjects. They found that the food  A recent research project used particles called peptides to identify how introducing certain molecules into the gut microbiome affected cholesterol levels in the body. Using mice that were fed high-fat diets and bred to develop arterial plaque, the team used peptides to alter the health of the gut microbiome and, in turn, improve cholesterol levels.
A recent research project used particles called peptides to identify how introducing certain molecules into the gut microbiome affected cholesterol levels in the body. Using mice that were fed high-fat diets and bred to develop arterial plaque, the team used peptides to alter the health of the gut microbiome and, in turn, improve cholesterol levels. There are two primary ways to ensure you’re introducing sufficient quantities of probiotics and prebiotics into your gut microbiome. Many
There are two primary ways to ensure you’re introducing sufficient quantities of probiotics and prebiotics into your gut microbiome. Many  It is now well-known that obesity raises the
It is now well-known that obesity raises the  The glycemic index ranks foods based upon the effects they have on blood sugar levels. Foods that have a
The glycemic index ranks foods based upon the effects they have on blood sugar levels. Foods that have a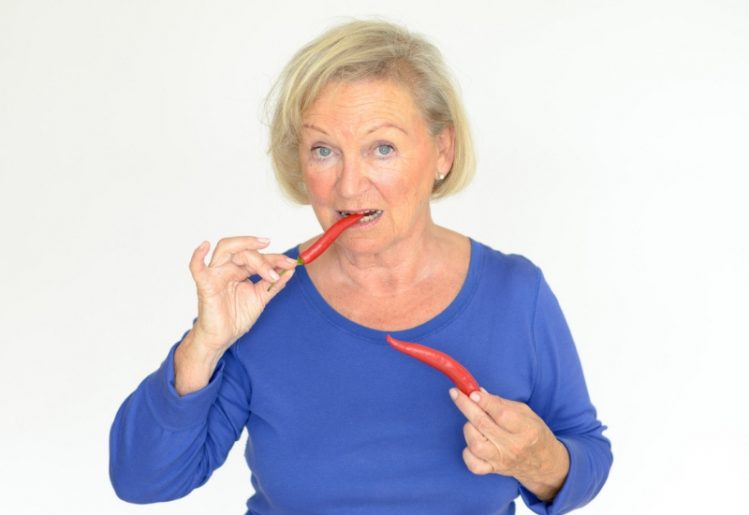  The reason capsaicin has gained the attention of researchers in the United States is that there are lower instances of cancer in countries where spicy dishes are more common. Thailand and India in particular have lower numbers of lung cancer cases. Seeking to understand if there was a link between spicy foods and cancer, researchers began investigating and found that capsaicin seemed to be the common factor.
The reason capsaicin has gained the attention of researchers in the United States is that there are lower instances of cancer in countries where spicy dishes are more common. Thailand and India in particular have lower numbers of lung cancer cases. Seeking to understand if there was a link between spicy foods and cancer, researchers began investigating and found that capsaicin seemed to be the common factor. We experience pain because our nerves carry pain messages to the brain. This process is aided by the release of a chemical called substance P. It has been found that capsaicin helps exhaust the supply of substance P, making it more difficult for your nerves to carry those pain messages back to the brain. To prove this effect, researchers administered 2.5 grams of capsaicin to heartburn sufferers on a daily basis. Initially, the heartburn pain worsened, but it improved significantly after the first few days.
We experience pain because our nerves carry pain messages to the brain. This process is aided by the release of a chemical called substance P. It has been found that capsaicin helps exhaust the supply of substance P, making it more difficult for your nerves to carry those pain messages back to the brain. To prove this effect, researchers administered 2.5 grams of capsaicin to heartburn sufferers on a daily basis. Initially, the heartburn pain worsened, but it improved significantly after the first few days.