Colorectal cancer amounts for about 700,000 deaths worldwide. Could taking a daily dose of a certain supplements offer protection while also promoting stronger brain and heart health? A new study from the UK called the 2018 seAFOod Trial that discovered a link between aspirin, omega-3 and colon cancer supports this theory.
Colon Cancer, Polyps, and Pre-cancerous Conditions
 The National Cancer Institute anticipates over 140,000 new cases of colon-related cancer in the U.S. by the end of 2018. Colon cancer affects men and women equally, with the average age of diagnosis being 67. The current mortality rate is 14 percent. Colon cancer typically begins with adenomatous polyps (adenomas), but their presence alone isn’t enough for a cancer diagnosis. People can have these pre-cancerous polyps and never have cancer. However, their presence in the colon does greatly increase a person’s risk for developing colorectal-types of cancer. Other risk factors include polyp size, the number of polyps and dysplasia after a biopsy. Age and lifestyle are the two largest risk factors for colon cancer. Family history of colorectal cancer is the third leading factor, followed by other bowel related diseases.
The National Cancer Institute anticipates over 140,000 new cases of colon-related cancer in the U.S. by the end of 2018. Colon cancer affects men and women equally, with the average age of diagnosis being 67. The current mortality rate is 14 percent. Colon cancer typically begins with adenomatous polyps (adenomas), but their presence alone isn’t enough for a cancer diagnosis. People can have these pre-cancerous polyps and never have cancer. However, their presence in the colon does greatly increase a person’s risk for developing colorectal-types of cancer. Other risk factors include polyp size, the number of polyps and dysplasia after a biopsy. Age and lifestyle are the two largest risk factors for colon cancer. Family history of colorectal cancer is the third leading factor, followed by other bowel related diseases.
Prevention and Early Detection
The prevention and early detection of cancer have become growing areas of study. These various preventive measures are popular among high-risk populations, but colon cancer doesn’t appear to disparage by race or sex, though some studies suggest a higher prevalence in men and African Americans.
Doctors recommend lifestyle changes at the earliest signs of pre-cancerous conditions, patient-revealed family history or diagnosis. The recommendations made wholly depend on the patient’s current lifestyle, but some suggestions could be to increase physical activity, overhauling the diet, quitting smoking and taking certain supplements.
Understanding the Role of Omega-3 Fatty Acid in Colon Cancer Prevention and Treatments
Taking omega-3 fatty acids might not be enough to prevent cancer alone, according to this review of available research at the time (which doesn’t take the new 2018 UK study into account). However, their overall health benefits to the heart, brain and digestive system when utilized along with healthy lifestyle changes and diet can provide essential building blocks for disease prevention.
Most omega-3 studies revolve around fish oil supplements or marine sources. One problem here is dissecting the omega-3 fatty acid chains and studying individual ones. Regardless, the eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) in omega-3 has shown promising results in studies for treating early colorectal cancer stages. It may also provide benefits for later stages as well as prevention. A treatment plan that includes EPA can also work alongside chemotherapy without adverse side effects.
What science and medicine know about omega-3 chains as a whole is that they help modulate inflammation in the body — and inflammation and colon cancer do seem to share a link. Some research has suggested that omega-3 fatty acids may have the ability to affect cancer cells and tumor size, but more studies are needed.
Omega-3 and Colon Cancer Prevention and Disease Mortality Decline
In the recent pre-cancerous polyp study that used aspirin and omega-3 supplements, four groups of participants were studied. Among the four groups, one group took aspirin and omega-3 supplements. Another took only aspirin while a third used only omega-3 supplements. The fourth group was a control. This particular study found that the combination of omega-3 and aspirin appeared to reduce the size of pre-cancerous polyps.
Two U.S.-based studies also analyzed data from high-risk men and women taking preventative treatments with or without a colon cancer diagnosis. During the extensive studies, over 1,600 people developed cancer, and over 500 of those passed away due to their disease. The participants who obtained a diagnosis and consumed omega-3 from fish sources saw a decrease in mortality rate. Scientists noted that among those who changed their dietary habits to include more omega-3 fatty acids after their diagnosis also had a reduction in death rate.
Concerns Over Aspirin and Omega-3 EPA Use
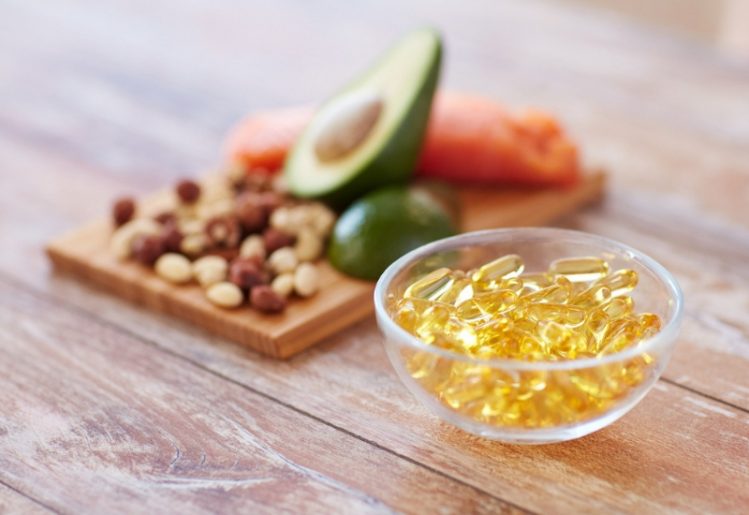 Doctors do raise concerns over taking a high dose of aspirin (300 mg) on an ongoing basis, which can cause internal bleeding. The study doesn’t include data for those with increased bleeding disorders, allergies to aspirin or stomach ulcers.
Doctors do raise concerns over taking a high dose of aspirin (300 mg) on an ongoing basis, which can cause internal bleeding. The study doesn’t include data for those with increased bleeding disorders, allergies to aspirin or stomach ulcers.
Aside from a temporary upset stomach and a fishy aftertaste, no known side effects or concerns arise with using dietary or therapeutic doses of omega-3 supplements. Some non-symptom concerns are the quality and increased caloric intake from supplements. High intakes beyond the scope of colon cancer studies do carry an increased risk of bleeding and possibly stroke. The new research shows promise when it comes to both treatment options and mortality rates in those with colon cancer. More studies could help further define the benefits when it comes to prevention and reoccurence rates as well.
Current guidelines suggest daily intake of omega-3 rich foods and taking supplements under a doctor’s guidance. For people who are at high risk of colon cancer, they should speak with their doctor about using the aspirin and/or aspirin and omega-3 therapy as a preventative measure. They should also be sure to continue with normal checkups and screening to catch any changes early.
 One of the newest discoveries is that black pepper extract benefits include helping the body process nutrients more efficiently. It does this by slowing down processes in the liver and intestines, allowing certain compounds to be held in the intestines longer. This gives the body more time to absorb nutrients, which allows the digestive system an opportunity to make better use of the foods we eat. Specifically, a process called “glucuronidation” is inhibited when piperine is added to the system. Under normal circumstances, glucuronidation helps the liver process medications and dietary supplements more rapidly. This process causes the beneficial properties of these substances to be flushed out with our urine prematurely. By arresting this process, the black pepper extract gives the body a longer period during which it can absorb these helpful properties of nutrients, vitamins and minerals that are ingested.
One of the newest discoveries is that black pepper extract benefits include helping the body process nutrients more efficiently. It does this by slowing down processes in the liver and intestines, allowing certain compounds to be held in the intestines longer. This gives the body more time to absorb nutrients, which allows the digestive system an opportunity to make better use of the foods we eat. Specifically, a process called “glucuronidation” is inhibited when piperine is added to the system. Under normal circumstances, glucuronidation helps the liver process medications and dietary supplements more rapidly. This process causes the beneficial properties of these substances to be flushed out with our urine prematurely. By arresting this process, the black pepper extract gives the body a longer period during which it can absorb these helpful properties of nutrients, vitamins and minerals that are ingested. In addition to helping the body flush excess water and toxins from the body, black pepper plants assist in
In addition to helping the body flush excess water and toxins from the body, black pepper plants assist in  For reasons that doctors and scientists do not fully understand, an increasing number of people are
For reasons that doctors and scientists do not fully understand, an increasing number of people are  Melatonin is important to the fertility of women, but it also appears to play a role in the fertility of men. High melatonin levels have been
Melatonin is important to the fertility of women, but it also appears to play a role in the fertility of men. High melatonin levels have been 
 In findings that were published earlier this year in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, a team of Norwegian researchers from the University of Bergen revealed that vitamin D
In findings that were published earlier this year in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, a team of Norwegian researchers from the University of Bergen revealed that vitamin D  A long-term deficiency carries a significant risk of permanent brain and nerve damage. B12 deficiency has been known to put some people at a higher risk of mental health issues such as dementia, mania or psychosis. A B12 deficiency also impacts immune response and can increase susceptibility to infection or disease. Long-term deficiency leads to the onset of anemia, which may be accompanied by any number of symptoms:
A long-term deficiency carries a significant risk of permanent brain and nerve damage. B12 deficiency has been known to put some people at a higher risk of mental health issues such as dementia, mania or psychosis. A B12 deficiency also impacts immune response and can increase susceptibility to infection or disease. Long-term deficiency leads to the onset of anemia, which may be accompanied by any number of symptoms: