Omega-3 fatty acids play a variety of roles in the body, contributing to both physical health and mental wellness. A new body of research is proving that supplementing with omega-3 protects against stress, helping to slow the aging process of the body as a result. Here is everything that you need to know about this class of fatty acids, including how you can boost your intake of this nutrient for better health.
What are Omega-3 Fatty Acids?
 You do not have to be a health nut to know that omega-3 fatty acids are one of the most important nutrients that you can give your body. But what exactly are these fatty acids and how do they benefit your body?
You do not have to be a health nut to know that omega-3 fatty acids are one of the most important nutrients that you can give your body. But what exactly are these fatty acids and how do they benefit your body?
There are three types of omega-3 fatty acids. Alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) is primarily found in plant oils such as canola oil and soybean oil. Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) are generally found naturally in fish and other types of seafood. As an essential fatty acid, your body does not make ALA, meaning that you must be diligent about getting it from food and beverage sources or through the use of targeted supplements.
Benefits of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
There is no shortage of benefits of omega-3 fatty acids. These nutrients can have a profound impact on the proper function of many parts of your body and brain. Sufficient intake of omega-3 is useful in fighting inflammation and in boosting bone health, helping to ward off conditions such as osteoporosis.
Because DHA is a primary structural component of the retinas in your eyes, maintaining adequate levels can be beneficial in preventing macular degeneration. Getting enough omega-3 fatty acids can also help to guard against a variety of chronic diseases and illnesses, including arthritis, heart disease and metabolic syndrome. The nutrient will also protect against autoimmune diseases such as type 1 diabetes, multiple sclerosis, ulcerative colitis, Crohn’s disease and psoriasis.
Taking in enough omega-3 fatty acids promotes better sleep while also improving the appearance of your skin. Finally, you will also reduce your risk of a host of mental disorders by boosting your intake of omega-3sm including depression, anxiety and the onset of Alzheimer’s disease.
It is clear that many areas of both your physical and mental health will benefit by being intentional about getting enough of this crucial nutrient.
How Supplementing With Omega-3 Protects Against Stress
A new study out of the Ohio State University revealed that daily supplements boasting 2.5 grams of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids performed the best when looking to help the body ward off the effects of stress. By suppressing the damage that stress can cause to the body and increasing protection at the cellular level, omega-3s can even potentially help to slow down the aging process.
The results of the study demonstrate that taking an omega-3 supplement is one of the easiest yet most profound ways that you can disrupt the cycle of stress on the body leading to a variety of health issues. A simple supplement is an easy way to ward off or in some cases even reverse some of the most significant health conditions that many people face.
While the 2.5-gram dose of omega-3s studied in this research is significantly more than what most people ingest on a daily basis, it is important to note that the participants in the study did not demonstrate any issues with the higher dosage.
How You Can Boost Intake of Omega-3 Fatty Acids
It is probably easier than you think to boost your intake of omega-3 fatty acids. Start your efforts by being intentional about incorporating the foods that are rich in this nutrient into your diet. Both flaxseed oil and canola oil are high in ALA omega-3s. Sprinkling chia seeds and walnuts on to your favorite foods will also boost your intake of omega-3 fatty acids.
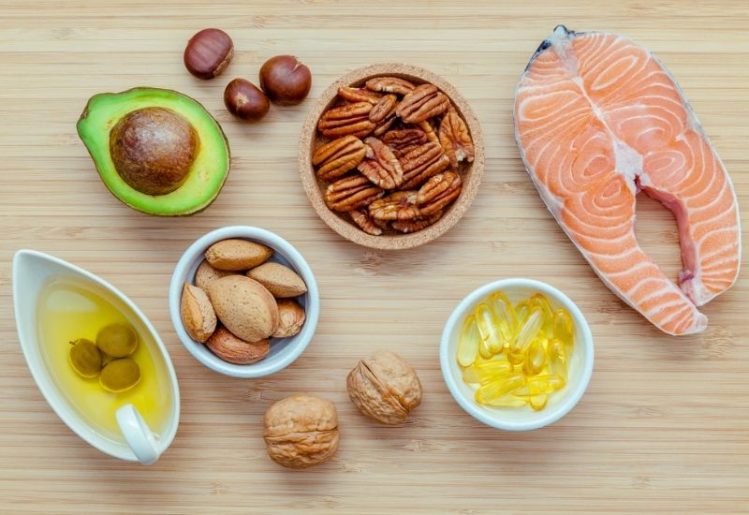 While nearly all seafood contains omega-3s, some sources are more nutrient dense than others. Salmon is a particularly rich source of omega-3 fatty acids. Herring, sardines and shellfish such as lobster and scallops also supply this nutrient. Next time you make a sandwich, consider spreading a tablespoon of mayonnaise on the bread to increase your intake of omega-3 fatty acids.
While nearly all seafood contains omega-3s, some sources are more nutrient dense than others. Salmon is a particularly rich source of omega-3 fatty acids. Herring, sardines and shellfish such as lobster and scallops also supply this nutrient. Next time you make a sandwich, consider spreading a tablespoon of mayonnaise on the bread to increase your intake of omega-3 fatty acids.
Because some of these top sources of omega-3s are not widely consumed by everyone, many health-savvy individuals turn to high-quality dietary supplements that provide omega-3 fatty acids to boost their intake of this important nutrient. As the recent study out of the Ohio State University proved, omega-3 fatty acids are easily processed by the body when consumed via supplements.
While there are still questions surrounding how to best harness the power of this nutrient, it is clear that omega-3 fatty acid should be an essential part of your health routine. The recent research detailing how omega-3s can protect against stress and slow the aging process is just another in a long list of compelling reasons why you should make the intake of this nutrient a priority for your health and wellness.
 The most convincing reason to make exercise a part of your lifestyle is because it has been proven to prolong your life.
The most convincing reason to make exercise a part of your lifestyle is because it has been proven to prolong your life.  Many people erroneously believe that exercise will make you hungrier. However, numerous studies have demonstrated that aerobic exercise actually decreases your overall appetite. This happens as a result of the effect of exercise on the hormones that control your hunger levels.
Many people erroneously believe that exercise will make you hungrier. However, numerous studies have demonstrated that aerobic exercise actually decreases your overall appetite. This happens as a result of the effect of exercise on the hormones that control your hunger levels. NAD takes two forms, depending on what point in the energy production cycle it is. These two forms are NAD+ and NADH. NAD levels decrease with age, contributing to the mitochondrial inefficiency and deterioration
NAD takes two forms, depending on what point in the energy production cycle it is. These two forms are NAD+ and NADH. NAD levels decrease with age, contributing to the mitochondrial inefficiency and deterioration  In animal studies and test tube studies done with
In animal studies and test tube studies done with  Omega-3 fatty acids
Omega-3 fatty acids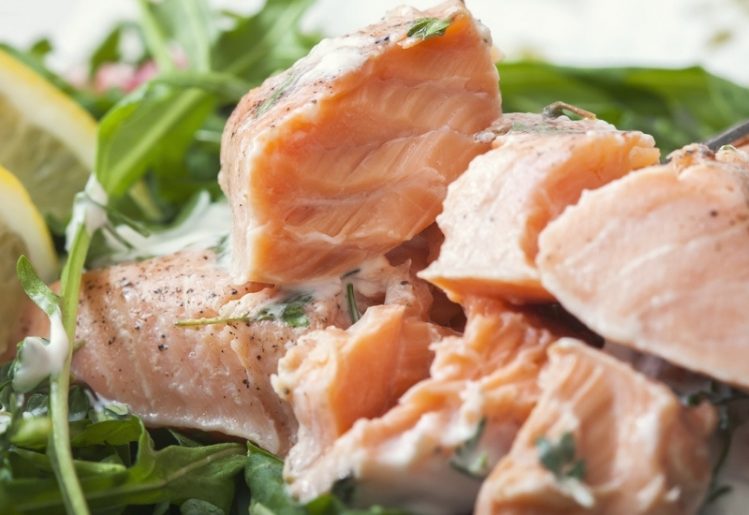 Ingredients
Ingredients
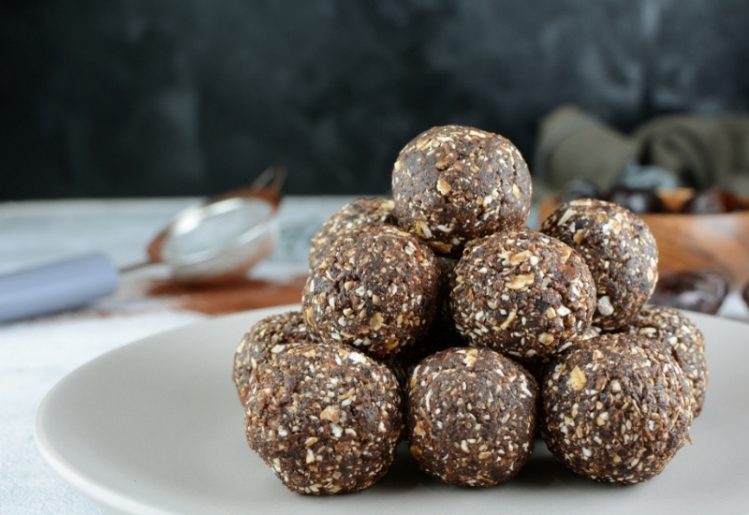 These yummy and nutritious no-bake energy balls can be enjoyed as a snack or healthy dessert by adults and kids alike.
These yummy and nutritious no-bake energy balls can be enjoyed as a snack or healthy dessert by adults and kids alike.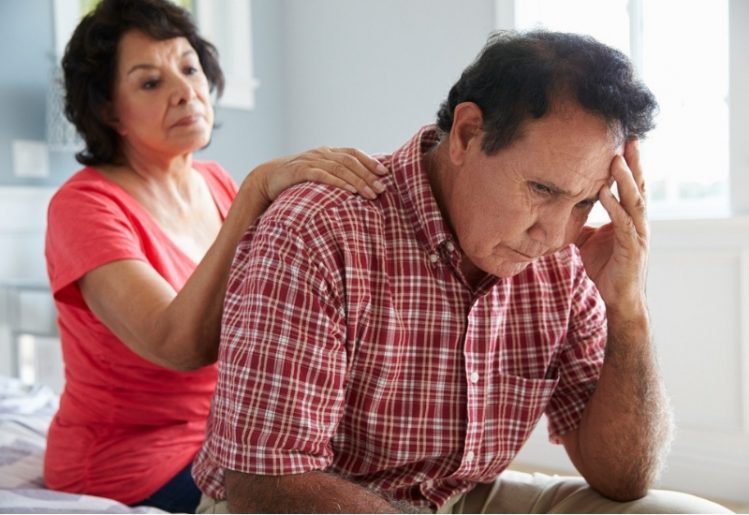 Dementia describes a cluster of symptoms that affect cognition, memory and social interaction to the extent that one’s daily life is disrupted. There are
Dementia describes a cluster of symptoms that affect cognition, memory and social interaction to the extent that one’s daily life is disrupted. There are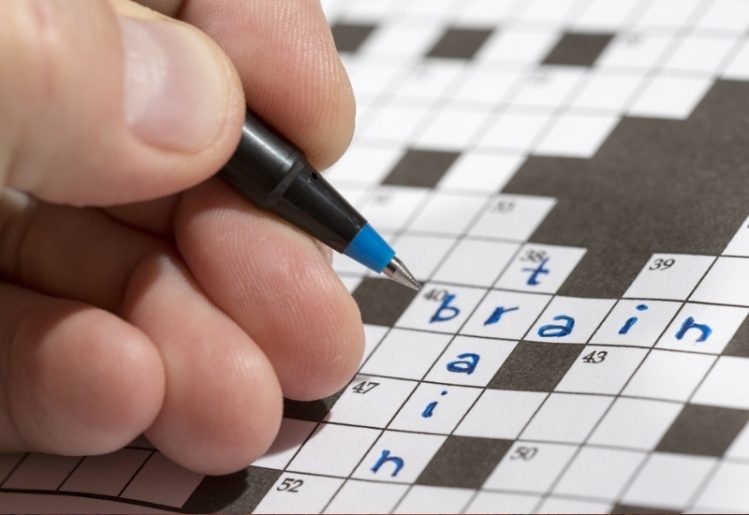  In addition to nurturing your mind through social connections, you can also stimulate your brain through mental exercises. Research has demonstrated a link between mental exercises and a lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Good activities to stretch your brain include reading, doing puzzles, playing card games and listening to music.
In addition to nurturing your mind through social connections, you can also stimulate your brain through mental exercises. Research has demonstrated a link between mental exercises and a lower risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease. Good activities to stretch your brain include reading, doing puzzles, playing card games and listening to music.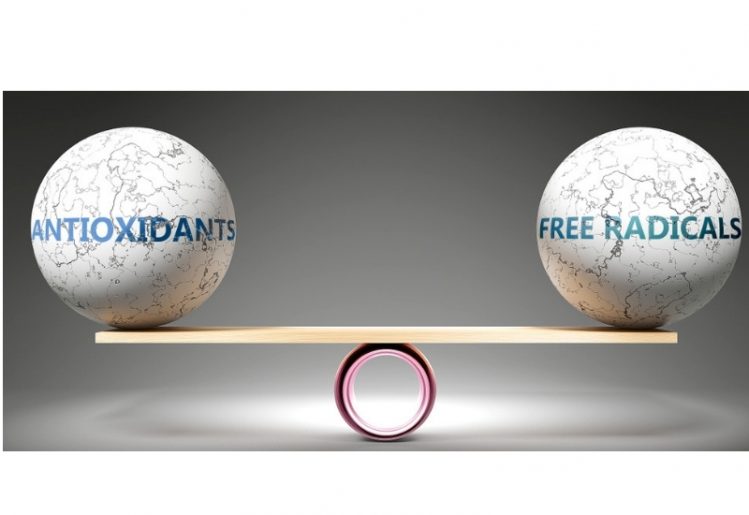 In its most basic definition, melatonin is a hormone produced by the body’s pineal gland. The
In its most basic definition, melatonin is a hormone produced by the body’s pineal gland. The  In order to boost production of melatonin in the evening, you need to increase the levels of serotonin in the morning. You can support serotonin production by exposing your body to sunlight in the morning.
In order to boost production of melatonin in the evening, you need to increase the levels of serotonin in the morning. You can support serotonin production by exposing your body to sunlight in the morning.