While you may not be familiar with whole body vibration, or WBV, it’s a practice that has been around for several decades. New research has found that whole body vibration benefits include a reduction in inflammation, while it also promotes a healthier gut microbiome.
What is Whole Body Vibration?
 Initially introduced in the early 1990s, whole body vibration is a form of passive exercise that involves using vibrations to send waves of energy through the entire body. The process involves standing, sitting or lying on a platform and enduring a series of vibrations. The vibrating energy causes your muscles to contract and expand repeatedly throughout the process, helping to grow and tone muscle mass. Daily 15 minute sessions may promote weight loss, improve blood flow and decrease the production of stress hormones.
Initially introduced in the early 1990s, whole body vibration is a form of passive exercise that involves using vibrations to send waves of energy through the entire body. The process involves standing, sitting or lying on a platform and enduring a series of vibrations. The vibrating energy causes your muscles to contract and expand repeatedly throughout the process, helping to grow and tone muscle mass. Daily 15 minute sessions may promote weight loss, improve blood flow and decrease the production of stress hormones.
In one recent study, subjects were divided into two groups, and each group had their oxygen intake and energy usage measured during physical activity. The subjects in the first group were subjected to WBV treatments before the trial, while the second group did not participate in WBV activities.
The researchers found that those subjects who received the whole body vibrations experienced over 22 percent greater oxygen intake and 20 percent greater energy usage. This indicates that the use of WBV along with a regular exercise routine may promote greater weight loss.
Additional research has found that whole body vibration benefits also include reversing conditions such as fatty liver disease and glucose intolerance. It has also been found to be effective in alleviating back pain, reducing bone loss and improving muscle coordination in senior adults. As more studies are conducted, there’s hope that WBV treatments will be effective in promoting better health in other ways.
New Research Pinpoints Whole Body Vibration Benefits
A recent study at Augusta University in Georgia focused on discovering why and how WBV treatments improve metabolic health, after discovering the positive effects it exhibited for type 2 diabetics. The research project involved studying mice with leptin deficiencies, since this abnormality raises the risk for obesity and insulin resistance. Obesity and insulin resistance both increase the risk of type 2 diabetes, so the researchers sought out test mice that exhibited these characteristics.
The study involved examining the microphages in the mice, which are cells in the immune system that are associated with the gut microbiome and general body inflammation. The mice were separated into a control group and a test group, with the mice in the test group receiving daily WBV treatments for a period of four weeks. At the end of the four weeks, each of the mice was evaluated by taking body fat and stool samples for analysis.
One of the findings involved an increased diversity in the gut microbiome, which helped reduce inflammation. In particular, the presence of alistipes, a type of bacteria that promotes the production of short-chain fatty acids in the body, was increased. These short-chain fatty acids are able to attack inflammation and reduce its presence wherever it occurs in the body. This bacteria is also responsible for helping the body extract butyrate from daily fiber, which helps reduce the dangers of a high-fat diet.
Whole body vibration helped to combat inflammation in the mice in another way; by increasing the presence of M2 macrophages. These immune cells are tasked with increasing the anti-inflammatory cytokines, and as a result, new inflammation is suppressed. The researchers found that shorter WBV sessions that were combined with alistipes supplements also helped improve metabolic health. Although they admit that more research is needed in this area, they feel hopeful that regular WBV treatment can help people reach and maintain more optimal metabolic health.
How Can You Protect Your Gut Microbiome?
Eat a Diverse Plant-Based Diet
Most of your meals should be comprised of plant-based foods, such as vegetables, fruits, seeds and nuts. You should also try to pick a variety of foods by choosing fruits and veggies with a broad range of colors. This will ensure you get a good sampling of vitamins, while also exposing your gut microbiome to a more diverse selection of helpful microbes.
Eat High-Fiber Foods
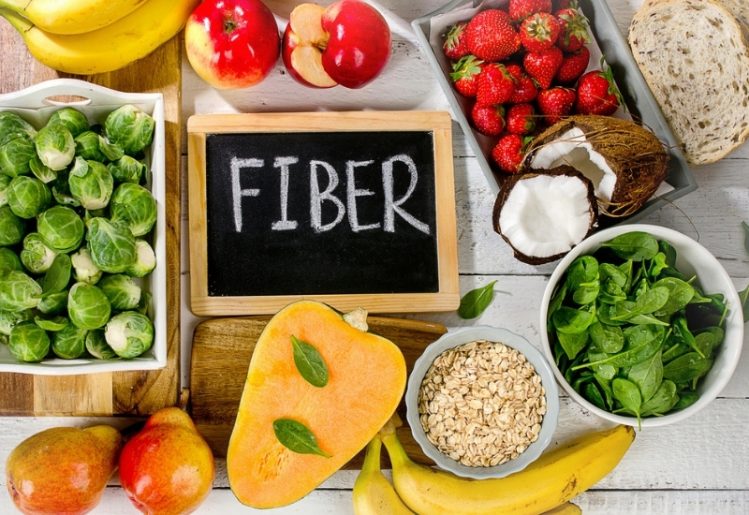 Some foods that are high in fiber include onions and similar foods, such as leeks and garlic. Artichokes are also high-fiber foods. Eating more of these types of veggies will help, because it takes longer for the body to digest natural fiber. As a result, the prebiotics in the fiber will be absorbed into the gut microbiome, where they nourish the bacteria already thriving there.
Some foods that are high in fiber include onions and similar foods, such as leeks and garlic. Artichokes are also high-fiber foods. Eating more of these types of veggies will help, because it takes longer for the body to digest natural fiber. As a result, the prebiotics in the fiber will be absorbed into the gut microbiome, where they nourish the bacteria already thriving there.
Fast Without Snacking
When you fast for several hours without snacking or drinking, you’ll be giving your gut microbiome an opportunity to rest. This will give that community of microbes an opportunity to do other work in your body, such as boosting immunity, so you’ll feel healthier. Additionally, weight gain is reduced overall by periods of fasting.
Take a Daily Probiotic/Prebiotic Supplement
There are high-quality supplements on the market that provide the body with a supply of both probiotics and prebiotics. Probiotic supplements supply “friendly” bacteria to the gut, and help promote a healthy and diverse gut microbiome. Once ingested, prebiotics are used by the gut microbiome to fortify the existing microbes in the body. This helps the gut microbiome function better and grow more diverse. Prebiotics can also boost colon health and improve digestive functions.
Spend More Time Outdoors
Improving the diversity of your gut bacteria will help you maintain better overall health, but eating more plant-based foods isn’t the only method. You can also expose your gut microbiome to more bacteria by spending more time outdoors, especially when you spend that time away from the city. Go to a favorite park or drive out to the country for the day. As you relax in nature, you’ll breathe in bacteria that your gut can use to manage your health.
 Diseases that affect the heart and blood vessels all fall under the broader term of cardiovascular disease, and many of those conditions are caused by atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a condition resulting from plaque accumulation on the walls of the arteries, which causes blood flow to become inhibited. Since blood flows more slowly, clots can form that block blood from passing through the arteries and reaching the brain, heart and other vital organs, boosting the probability that a stroke or heart attack will occur.
Diseases that affect the heart and blood vessels all fall under the broader term of cardiovascular disease, and many of those conditions are caused by atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a condition resulting from plaque accumulation on the walls of the arteries, which causes blood flow to become inhibited. Since blood flows more slowly, clots can form that block blood from passing through the arteries and reaching the brain, heart and other vital organs, boosting the probability that a stroke or heart attack will occur. Rather than eating three big meals every day, it’s important to eat wisely. It’s best to start off with a moderate breakfast that includes good natural sources of protein and fiber. An omelet that’s prepared with fresh veggies is one suggestion. For the remainder of the day, choose healthy snacks to munch on periodically, such as almonds, carrot sticks and cheese. This will help you eat less at dinner.
Rather than eating three big meals every day, it’s important to eat wisely. It’s best to start off with a moderate breakfast that includes good natural sources of protein and fiber. An omelet that’s prepared with fresh veggies is one suggestion. For the remainder of the day, choose healthy snacks to munch on periodically, such as almonds, carrot sticks and cheese. This will help you eat less at dinner. It is normal to
It is normal to  Although you want to take care to protect yourself from the sun’s harmful UV rays, a healthy amount of vitamin D will support the mitochondrial oxidative capacity in the body’s muscles.
Although you want to take care to protect yourself from the sun’s harmful UV rays, a healthy amount of vitamin D will support the mitochondrial oxidative capacity in the body’s muscles. Accounting for approximately 20 percent of an individual’s body weight
Accounting for approximately 20 percent of an individual’s body weight There are a number of steps that you can take to heal mitochondria or prevent future issues. Like most health issues, getting enough sleep, eating well, engaging in regular exercise and being diligent about reducing stressors in your life will all help to heal these damaged mitochondria.
There are a number of steps that you can take to heal mitochondria or prevent future issues. Like most health issues, getting enough sleep, eating well, engaging in regular exercise and being diligent about reducing stressors in your life will all help to heal these damaged mitochondria. In a normal, healthy gut microbiome, there up to 1,000 different types of bacteria. This is important, because each strain serves a different function, affecting health in a unique way. For instance, Bifidobacteria is a type of bacteria that helps infants digest the sugars that are present in breast milk. Similarly, other types of bacteria help the body digest fiber more efficiently. Once digested the compounds in fiber help the body protect against heart disease, cancer and obesity.
In a normal, healthy gut microbiome, there up to 1,000 different types of bacteria. This is important, because each strain serves a different function, affecting health in a unique way. For instance, Bifidobacteria is a type of bacteria that helps infants digest the sugars that are present in breast milk. Similarly, other types of bacteria help the body digest fiber more efficiently. Once digested the compounds in fiber help the body protect against heart disease, cancer and obesity. For many people, stress is increased by a lack of time to get everything accomplished. Even though you may have a lot on your plate, you can get through each day more easily by planning ahead. Just before bedtime each night, make a list of everything you need to get done on the following day and assign a block of time for each task. This will help to ensure you get everything done without feeling overly burdened.
For many people, stress is increased by a lack of time to get everything accomplished. Even though you may have a lot on your plate, you can get through each day more easily by planning ahead. Just before bedtime each night, make a list of everything you need to get done on the following day and assign a block of time for each task. This will help to ensure you get everything done without feeling overly burdened. One of the systems that regulates your overall health is the gut microbiome, which is located in your large intestines and serves as a home to trillions of microbes. While some bacteria can be harmful, the microorganisms in your gut microbiome are helpful, assisting your body by regulating digestion, immune system functioning and dozens of other processes throughout the body. While this system functions on its own, you can help it to work optimally by ensuring it has a broad and diverse community of microbes.
One of the systems that regulates your overall health is the gut microbiome, which is located in your large intestines and serves as a home to trillions of microbes. While some bacteria can be harmful, the microorganisms in your gut microbiome are helpful, assisting your body by regulating digestion, immune system functioning and dozens of other processes throughout the body. While this system functions on its own, you can help it to work optimally by ensuring it has a broad and diverse community of microbes. Essentially, prebiotics work together with probiotics to ensure your gut microbiome is as diverse as possible. If you think you may not be getting enough prebiotics and probiotics in your diet, taking a
Essentially, prebiotics work together with probiotics to ensure your gut microbiome is as diverse as possible. If you think you may not be getting enough prebiotics and probiotics in your diet, taking a