Prebiotics are insoluble fibers that, when ingested, help to nourish the beneficial bacteria in the gut. New evidence suggests that when consumed daily, prebiotics help reduce anxiety and boost overall mental health. Find out how you can help your gut microbiome by incorporating more prebiotics into your diet.
What’s the Difference Between Prebiotics and Probiotics?
 While certain bacteria are harmful to your health, there are also strands of bacteria that are beneficial to your health. These helpful types of bacteria thrive in the intestines, and they form a community known as the gut microbiome. The helpful bacteria that exists in the foods we eat are called probiotics. By eating a broader range of natural foods that contain probiotics, you help to increase the population of helpful bacteria in your gut. A more diverse selection of probiotics in your gut helps to manage weight, boost the immune system and regulate many other biological functions throughout the body.
While certain bacteria are harmful to your health, there are also strands of bacteria that are beneficial to your health. These helpful types of bacteria thrive in the intestines, and they form a community known as the gut microbiome. The helpful bacteria that exists in the foods we eat are called probiotics. By eating a broader range of natural foods that contain probiotics, you help to increase the population of helpful bacteria in your gut. A more diverse selection of probiotics in your gut helps to manage weight, boost the immune system and regulate many other biological functions throughout the body.
However, the “‘friendly” bacteria in your gut need nutrition to thrive and grow just like any other type of living organisms, and this is where prebiotics come in. Some of the plant-based foods we eat also contain certain types of fiber and other natural compounds that the human body can’t digest, which are known as prebiotics. Fortunately, the bacteria in your gut needs these compounds to survive.
Eating foods rich in prebiotic compounds will help grow the population of probiotics in your gut by giving them the sustenance they need to grow and multiply. In this way, probiotics and prebiotics form a process that’s beneficial to gut health and other aspects of your overall health. It also means that failing to eat enough foods that are rich in prebiotics can adversely affect your health by reducing the diverse range of probiotics in your gut.
How Can Prebiotics Help Reduce Anxiety?
The relationship between prebiotics and probiotics is important to understand in terms of mental health due to the recent findings in anxiety research. Even before the latest evidence was uncovered, researchers found that probiotics affect the brain’s ability to regulate mood. Additionally, probiotics are responsible for helping to manage stress before it has an opportunity to affect physical and emotional health. While it’s more commonly known that insufficient probiotics in the diet can lead to digestive disorders, including irritable bowel syndrome, it has also been found to increase the chances of developing depression, Alzheimer’s disease and other types of mental and emotional health problems.
Newer research has focused on how prebiotics help reduce anxiety when they are included as a consistent part of one’s diet. A recent study, conducted at the UK’s University of Surrey, focused on how prebiotic-rich foods affected a group of 64 healthy women between the ages of 18 and 25.
In the study, the group of women was divided in half with 32 receiving a daily prebiotic supplement. The women in the other group were given a placebo. Emotional health status among the women was evaluated by administering questionnaires to the subjects in both groups. The surveys inquired about mood changes, feelings of anxiety and sleep difficulties. The participants were also required to provide fecal samples to help researchers determine the health of each woman’s gut microbiome.
After 28 days, researchers found that the women taking the prebiotic supplements exhibited better gut health and reduced levels of anxiety. The women in the other group exhibited no changes in gut health or emotional health.
Dr. Kathrin Cohen Kadosh, who headed up the research project, concluded that the findings provided hope for improving both gut health and emotional health. She said that adding a prebiotic supplement to one’s daily routine could strengthen gut health, while also improving mental health. There’s also hope that this discovery may lead to new treatments for emotional and cognitive health problems in the future.
How Can You Add More Prebiotics to Your Diet?
There are a two primary ways to ensure you are getting sufficient amounts of beneficial prebiotics in your daily diet.
Take a Daily Supplement
You can directly introduce more prebiotics and probiotics into your gut by taking a high-quality daily supplement. Be sure to look for a supplement that contains a healthy supply of both probiotics and prebiotics, such as Florachron. This will ensure that you’re receiving all of the nutrients your gut needs to thrive and support your overall health.
Eat More Prebiotic-Rich Foods
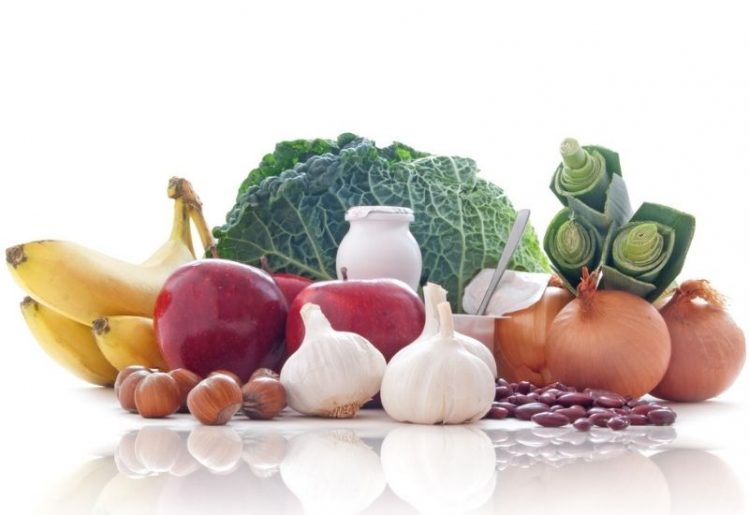 Essentially, look to incorporate prebiotic foods that have high amounts of natural fiber and natural carbohydrates. The body converts the fiber and carbs into butyrate, which is a short-chain fatty acid. Butyrate is used by the bacteria in the gut for nourishment.
Essentially, look to incorporate prebiotic foods that have high amounts of natural fiber and natural carbohydrates. The body converts the fiber and carbs into butyrate, which is a short-chain fatty acid. Butyrate is used by the bacteria in the gut for nourishment.
The best foods to eat for their prebiotic content are:
- legumes and beans
- peas
- bananas
- berries
- asparagus
- garlic, leeks and onions
Probiotics and prebiotics are not found in the same foods, making it important to develop a diet that includes a broad range of foods. For probiotics, you’ll need to eat more fermented foods, such as plain yogurt, sauerkraut, kimchi and unpasteurized pickles. Any fermented food you eat should be unpasteurized since the pasteurization process kills the beneficial bacteria in the food.
While research into the gut microbiome’s affects on mental health continues, we already know that a diverse gut microbiome positively impacts cognitive functioning, mood and emotional health. By taking steps to create a more diverse population of bacteria in your gut, you can improve many different aspects of your health, including alleviating anxiety and stress.
 Your gut microbiome
Your gut microbiome A study out of Kiel University has recently established a connection between the genetic variations that are responsible for your
A study out of Kiel University has recently established a connection between the genetic variations that are responsible for your  The gut microbiome
The gut microbiome It is important to keep in mind that the presence of bad bacteria helps to train your body to recognize what is a true danger. The overuse of sanitizing products deprives the immune system of the chance to react appropriately. Over-sanitizing can possibly lead to bacteria resistance and contribute to the development of superbugs. While you should wash your hands before eating and after using the bathroom, it is better to resist the temptation to over-sanitize.
It is important to keep in mind that the presence of bad bacteria helps to train your body to recognize what is a true danger. The overuse of sanitizing products deprives the immune system of the chance to react appropriately. Over-sanitizing can possibly lead to bacteria resistance and contribute to the development of superbugs. While you should wash your hands before eating and after using the bathroom, it is better to resist the temptation to over-sanitize. To understand how to use probiotics for weight loss, you need to learn more about
To understand how to use probiotics for weight loss, you need to learn more about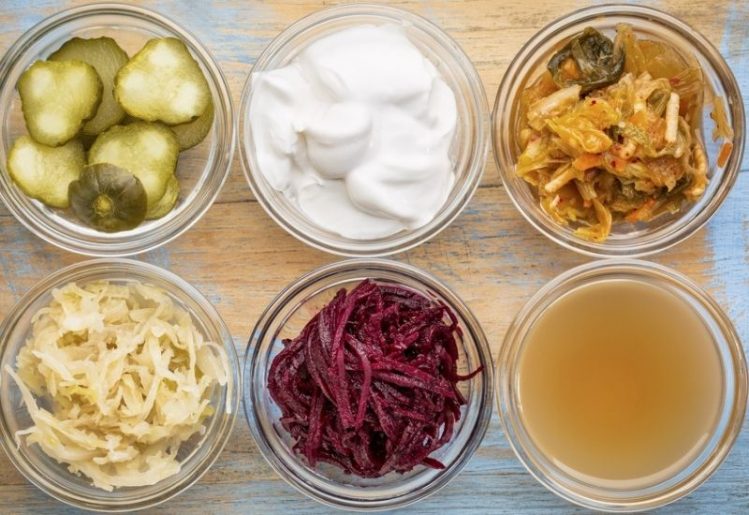  Up until the time when the use of supplements became mainstream, health-conscious individuals were forced to get their probiotics from food. The most common food that people turn to for probiotics is yogurt. However, it is important to note that not all yogurt contains live probiotics. Because of this, you need to be intentional about choosing yogurt that contains active or live cultures.
Up until the time when the use of supplements became mainstream, health-conscious individuals were forced to get their probiotics from food. The most common food that people turn to for probiotics is yogurt. However, it is important to note that not all yogurt contains live probiotics. Because of this, you need to be intentional about choosing yogurt that contains active or live cultures.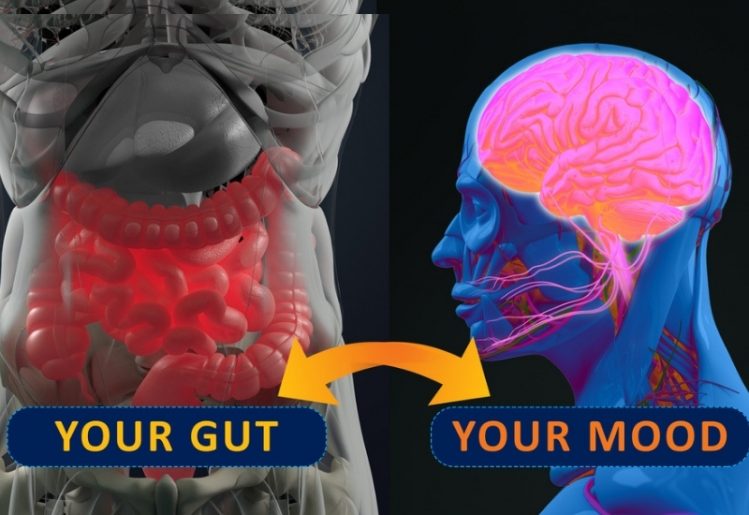 While there are already established links between gut microbiota and
While there are already established links between gut microbiota and  he daily diet is the key element when it comes to the health of the gut microbiome. In fact, researchers have been able to connect specific microbes to specific foods. In the future, that may be able to help produce detailed, food-specific diets to help people with a high risk of a particular disease reduce that risk via
he daily diet is the key element when it comes to the health of the gut microbiome. In fact, researchers have been able to connect specific microbes to specific foods. In the future, that may be able to help produce detailed, food-specific diets to help people with a high risk of a particular disease reduce that risk via  Aside from its role in building strong teeth and
Aside from its role in building strong teeth and  The
The