A new study published in the journal PNAS has uncovered the biology behind age-related bone loss. Researchers from Zhejiang University in China and the University of Alabama in Birmingham found that a protein known as Cbf-beta is essential at controlling the rate at which new bone cells replace old, dying cells.
Understanding Age-Related Bone Loss
Age-related bone loss is a progressive and serious disease that occurs when the body loses too much bone mass or produces too little new bone. This causes the bones to become weak and likely to break in a fall. In very serious cases, even minor bumps or sneezing can cause a fracture. Healthy bone resembles a honeycomb under a microscope. By comparison, bones that have lost mass have large spaces and holes.
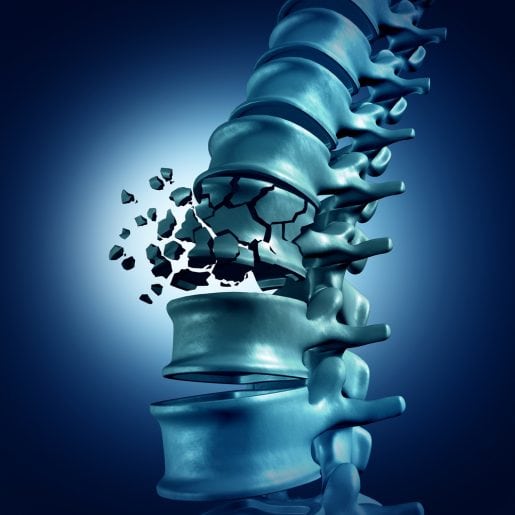 This disease is serious and potentially life-threatening. Fractures from bone loss are most likely to occur in the wrist, spine or hip, but they can happen anywhere. Bone loss can limit mobility and the complications can be life-threatening to older adults. 20 percent of seniors who break a hip bone die within a year from the corrective surgery or fracture.
This disease is serious and potentially life-threatening. Fractures from bone loss are most likely to occur in the wrist, spine or hip, but they can happen anywhere. Bone loss can limit mobility and the complications can be life-threatening to older adults. 20 percent of seniors who break a hip bone die within a year from the corrective surgery or fracture.
Age-related bone loss affects about 54 million people in the United States. It’s estimated that one in two women and one in four men over the age of 50 will suffer a bone fracture at some point due to bone loss. Women are four times more likely to develop bone loss as their bones are naturally thinner and they have a longer lifespan. Menopause, which stops estrogen production that helps use calcium, also plays a big role.
Risk factors for age-related bone loss include:
- Age. Bone density peaks around 30. After that, bone mass begins to decline. This makes it more important to exercise and get enough vitamin D and calcium to maintain bone mass.
- Family history.
- Gender. Women are far more likely to develop bone loss.
- Body weight and bone structure. Women who are thin and petite are more likely to lose bone mass than women with a larger frame.
- Ethnicity. Asian and Caucasian women have a higher risk of bone loss than other ethnic groups.
- Diseases like rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
- Certain medications like steroids.
- Smoking.
- Heavy drinking.
The Mechanism Behind Osteoporosis Revealed
Previous research has found that progenitor cells, or immature cells in the body, remain in reserve until receiving genetic instructions from transcription factors to become a new type of cell. When it comes to bone tissue, progenitor cells become bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Depending on the genetic instructions, mesenchymal stem cells may mature into cartilage-producing cells (chondrocytes), bone-producing cells (osteoblasts) or fat cells (adipocytes).
In the recent study, after investigating transcription factors that control how progenitor cells mature, the researchers found that a protein called Cbf-beta was necessary to switch between bone-producing cells and fat cells. Until this study, it was unknown what controlled how progenitor cells matured to maintain the balance of bone formation.
This study involved engineering three groups of mice by deleting the Cbf-beta protein at different stages of progenitor cell maturation. All three groups of mice developed severe bone loss and accumulated fat in the bone marrow, much like the age-related bone loss in humans. This also led to increased levels of fat cell genes in progenitor cells and bone cells in the skulls of the mice without Cbf-beta.
After further research, the teams found that Cbf-beta works by activating a signal in a cell that blocks expression of the gene that causes progenitor cells to turn into fat cells. The researchers hope that this discovery will eventually lead to new ways to treat bone loss.
How to Guard Against Bone Loss
 While bone loss begins to occur gradually as we age, there are many ways to protect healthy bone production. Staying active is one of the most important ways to protect your bones. The Cleveland Clinic recommends a specific exercise regimen for people with bone loss who have not suffered a fracture. This includes cardiovascular workouts and strengthening exercises.
While bone loss begins to occur gradually as we age, there are many ways to protect healthy bone production. Staying active is one of the most important ways to protect your bones. The Cleveland Clinic recommends a specific exercise regimen for people with bone loss who have not suffered a fracture. This includes cardiovascular workouts and strengthening exercises.
Eating a healthy diet high in nutrients necessary to build bone and supplementing as necessary can ensure your body has what it needs to form new bone cells. The following are the most important nutrients for healthy bones.
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is produced by the body after exposure to sunlight, but it can be found in some foods. Vitamin D deficiency is common in the United States and elsewhere. Vitamin D supplementation is often recommended to achieve recommended daily levels.
Calcium
Calcium is necessary for healthy growth and development of bones. Good calcium intake is also essential to achieve peak bone mass and it can modify the rate of bone loss as we age. Unfortunately, many adults in the United States fail to achieve the recommended daily calcium intake.
Vitamin K
Vitamin K has recently been found to play an important role in bone metabolism and bone health. Blood levels of vitamin K have even been found to be an indicator of hip fractures.
Phytoestrogens
Estrogen deficiency is one of the biggest contributing factors to the high rate of bone loss in post-menopausal women. This is why estrogen replacement therapy is still the only proven way to prevent and help reverse bone loss. Phytoestrogens may be a safer alternative. Also known as dietary estrogen, phytoestrogens are compounds that naturally occur in plant foods and structurally resemble natural estrogen.
MSM
Methylsulfonylmethane or MSM is a sulfur-containing compound that’s found in grains, vegetables and fruits. This antioxidant is believed to reduce swelling and oxidative damage, especially after strenuous activities like exercising. One study conducted at the Department of Orthopedics at Assaf Harofeh Medical Center in Israel found that patients who used MSM for 12 weeks reported an improvement in osteoarthritic symptoms.
Magnesium
While magnesium does not directly help bone growth, it is necessary to absorb calcium and MSM. Magnesium is necessary to convert vitamin D into its active form so it can activate calcium absorption.
Supplementing these important nutrients or a high-quality formula that provides two or more of these ingredients can help protect bone health as you age.
 Lutein is one of 600 carotenoids that’s often called the “eye vitamin” for its use in the prevention of eye diseases. This antioxidant is responsible for giving vegetables and fruits their yellow color. Lutein can only be obtained through diet and supplements; it isn’t produced by the human body.
Lutein is one of 600 carotenoids that’s often called the “eye vitamin” for its use in the prevention of eye diseases. This antioxidant is responsible for giving vegetables and fruits their yellow color. Lutein can only be obtained through diet and supplements; it isn’t produced by the human body. This is not the first study involving lutein and cognitive aging. Another study, published in the
This is not the first study involving lutein and cognitive aging. Another study, published in the  If you want to get your skin ready to be bared, there are several natural ingredients that can help you on your way. Consider taking a supplement that contains some of the following skin-friendly vitamins and herbs:
If you want to get your skin ready to be bared, there are several natural ingredients that can help you on your way. Consider taking a supplement that contains some of the following skin-friendly vitamins and herbs: Resveratrol has recently become popular due to its
Resveratrol has recently become popular due to its  How can a simple grape extract help promote healthy respiratory aging and protect against certain lung concerns? The antioxidant effects of resveratrol are believed to be one of its major benefits. In one study, when mice were given inhaled resveratrol, they saw
How can a simple grape extract help promote healthy respiratory aging and protect against certain lung concerns? The antioxidant effects of resveratrol are believed to be one of its major benefits. In one study, when mice were given inhaled resveratrol, they saw  Some people keep their mental faculties throughout old age, while others succumb to Parkinson Disease, Alzheimer’s disease and other devastating types of dementia. Most elderly people end up somewhere between these two extremes, with a condition known as
Some people keep their mental faculties throughout old age, while others succumb to Parkinson Disease, Alzheimer’s disease and other devastating types of dementia. Most elderly people end up somewhere between these two extremes, with a condition known as  Ultimately, a healthy body requires a variety of different nutrients to achieve optimal health. However, the Western diet tends to be deficient in these nutrients, contributing to the epidemic of chronic disease that currently is overtaking many developed nations. While we have ample access to a variety of foods, many people cannot or simply do not get the zinc they need to protect their DNA.
Ultimately, a healthy body requires a variety of different nutrients to achieve optimal health. However, the Western diet tends to be deficient in these nutrients, contributing to the epidemic of chronic disease that currently is overtaking many developed nations. While we have ample access to a variety of foods, many people cannot or simply do not get the zinc they need to protect their DNA.