Inflammation is one of the responses that the immune system produces to combat a foreign threat, such as a virus or an infection. In chronic inflammation, inflammation lingers for a long period of time — months or perhaps even years — possibly becoming an ongoing condition in the individual’s body. Chronic inflammation has been linked to a number of serious health concerns, including autoimmune disease, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, arthritis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and more. New research has discovered a link between anxiety and inflammation; although the question of whether anxiety causes inflammation or whether inflammation incites anxiety has yet to be answered, some research suggests that protecting against or reducing inflammation in the body may offer benefits for those who experience anxiety.
How Chronic Inflammation Harms Human Health
 Although in general, inflammation is a healthy response to infection or injury, chronic or long-lasting inflammation can eventually become detrimental to your health.
Although in general, inflammation is a healthy response to infection or injury, chronic or long-lasting inflammation can eventually become detrimental to your health.
For example, individuals with an unusually high number of markers for inflammation will also have a higher risk of developing chronic medical conditions. Health conditions like metabolic syndrome, obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease are more common in those who suffer from chronic inflammation. In addition to the symptoms of the particular disease an individual develops, chronic inflammation can also cause the symptoms like fatigue and body pain.
Causes and Contributing Factors
While the presence of autoimmune disease increases the likelihood that someone suffers from chronic inflammation, there are other factors to consider. If you meet any of these criteria, there’s a higher than average chance that you either suffer from chronic inflammation or will develop the condition in the future.
- are age 50 or older
- are overweight or obese
- consume a diet rich in unhealthy fats and sugar
- smoke cigarettes
- have low testosterone or estrogen levels
- suffer from stress or anxiety
- have a sleep disorder
There are other conditions that are often present in those with chronic inflammation. These conditions include asthma, tuberculosis, rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis. There’s some indication that a poor gut microbiome may also contribute to chronic inflammation. As a result, people who suffer from a chronic peptic ulcer, Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis may also be suffering from chronic inflammation.
Taking steps to alleviate inflammation may also help reduce the severity or frequency of symptoms for these other medical conditions. Alternatively, taking steps to boost the health of your gut microbiome may help reduce chronic inflammation.
New Research Finds a Link Between Anxiety and Inflammation
In a recent study, researchers examined a broad sample of subjects, looking for inflammation markers in their blood. They looked for the markers identified as CRP, IL-6, and TNF-alpha in each of the 853 subjects, recording the degree to which the markers were present in each subject. They also asked each of the individuals to complete a questionnaire that focused on the state of mind and level of anxiety each was experiencing.
Upon examining their findings, the research team discovered that men with higher levels of CRP, IL-6 and TNF-alpha also reported experiencing more severe anxiety. Similarly, women with higher levels of anxiety had more of the CRP and IL-6 markers in their blood.
Simply verifying that both inflammation and anxiety are present in the body at the same time still doesn’t prove that one causes the other. Attempting to show that there’s a stronger link between anxiety and inflammation, the researchers administered doses of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to the test subjects. LPS is a compound that’s known to trigger the immune system’s inflammatory reaction. As expected, inflammation markers in the blood of each subject increased significantly, with the IL-6 marker being the highest. It was also observed that anxiety levels in the participants increased to corresponding levels.
This research confirms the belief that inflammation may be a cause of anxiety and that by controlling chronic inflammation, anxiety may also be reduced. It also suggests that inflammation may increase the risk for diseases other than heart disease, diabetes and anxiety. In taking steps to reduce inflammation by introducing anti-inflammatory foods and nutrients into your diet, you may be able to lower your risk for anxiety and a broad range of other chronic conditions.
How Can You Reduce Inflammation Risk?
In general, processed foods should be avoided and replaced with more natural or plant-based foods. This is because processed foods contain high levels of refined carbs that lead to insulin resistance when consumed frequently or in high quantities. The result is an increase in the production of inflammatory cytokines in your body. Additionally, processed foods have high concentrations of omega-6 fatty acids, which are also an inflammatory agents when consumed out-of-proportion with the balancing omega-3 fatty acids.
Specifically, the following inflammatory foods should be avoided:
- refined carbs (white bread, baked goods, etc.)
- fried foods
- soda and other drinks that include high amounts of added sugar
- burgers, hot dogs and other types of processed meats
- margarine, lard and shortener
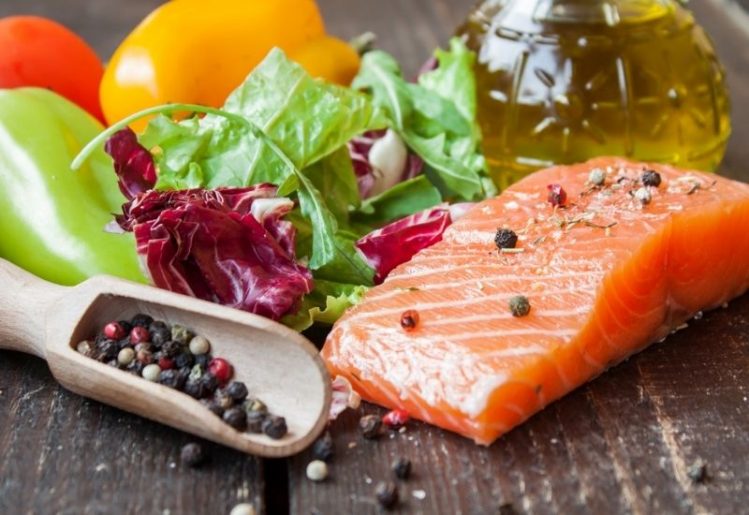 While all plant-based foods make better eating options, these particular foods provide specific anti-inflammatory benefits:
While all plant-based foods make better eating options, these particular foods provide specific anti-inflammatory benefits:
- tomatoes
- olive oil
- kale, spinach and other leafy greens
- nuts, including walnuts and almonds
- salmon, tuna, sardines and other types of oily fish
- fruits, including strawberries, cherries, blueberries and oranges
Even before research linked chronic inflammation with a state of anxiety, it was known that diet affects emotional health. People who eat more processed foods experience more depressive episodes and struggle with stress more frequently. They also feel anxiety more acutely.
On the opposite side of the same token, eating a Mediterranean diet, or a diet comprised largely of plant-based foods, has been shown to lead to better emotional and cognitive health. People who stick to a more natural diet feel generally happier and more energetic. They also experience lower levels of stress, which is also known to trigger feelings of anxiety. A number of natural nutrients may also help protect against inflammation. Supplementing your diet with a high-quality natural formula that provides these nutrients could also help in the battle against inflammation.
This latest research gives us a better understanding of how our diet influences emotional health, particularly feelings of anxiety.
 Fish oil is full of valuable omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids
Fish oil is full of valuable omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids A growing body of research indicates that people who struggle with depression may exhibit inadequate levels of omega-3 fatty acids. In addition, studies have demonstrated a link between low levels of fatty acids and cognitive decline. Other studies have shown that EPA and DHA may be helpful in fending off dementia, Parkinson’s disease and certain types of post-traumatic stress disorders.
A growing body of research indicates that people who struggle with depression may exhibit inadequate levels of omega-3 fatty acids. In addition, studies have demonstrated a link between low levels of fatty acids and cognitive decline. Other studies have shown that EPA and DHA may be helpful in fending off dementia, Parkinson’s disease and certain types of post-traumatic stress disorders. Vitamin D is most useful in supporting calcium absorption throughout the body, particularly in the gut. Vitamin D also works in tandem with calcium for
Vitamin D is most useful in supporting calcium absorption throughout the body, particularly in the gut. Vitamin D also works in tandem with calcium for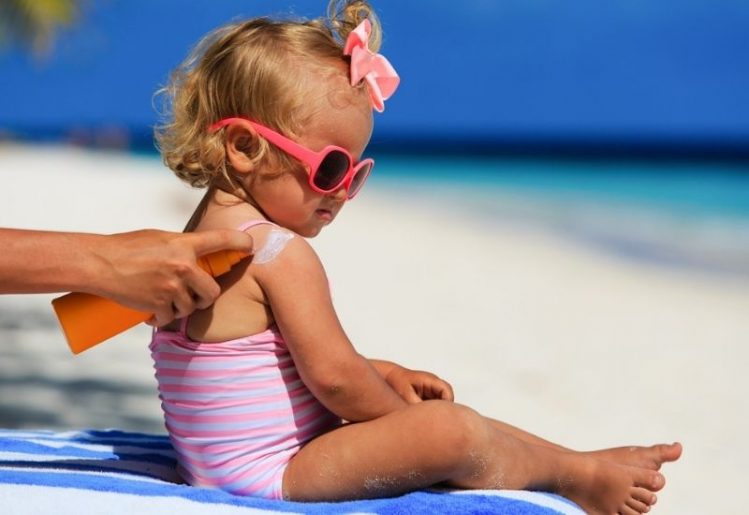  Because vitamin D is not as plentiful in foods as other vitamins, many people turn to the sun to deliver this nutrient. The challenge is finding that balance between sufficient protection from the sun and getting your daily dose of vitamin D.
Because vitamin D is not as plentiful in foods as other vitamins, many people turn to the sun to deliver this nutrient. The challenge is finding that balance between sufficient protection from the sun and getting your daily dose of vitamin D. The gut microbiome
The gut microbiome It is important to keep in mind that the presence of bad bacteria helps to train your body to recognize what is a true danger. The overuse of sanitizing products deprives the immune system of the chance to react appropriately. Over-sanitizing can possibly lead to bacteria resistance and contribute to the development of superbugs. While you should wash your hands before eating and after using the bathroom, it is better to resist the temptation to over-sanitize.
It is important to keep in mind that the presence of bad bacteria helps to train your body to recognize what is a true danger. The overuse of sanitizing products deprives the immune system of the chance to react appropriately. Over-sanitizing can possibly lead to bacteria resistance and contribute to the development of superbugs. While you should wash your hands before eating and after using the bathroom, it is better to resist the temptation to over-sanitize. During National Nutrition Month, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics takes center stage by providing a host of healthy eating goals and tips. The 2021 theme is Personalize Your Plate, encouraging people to create a myriad of nutritious meals to meet their own dietary needs and that also align with cultural preferences. The premise of the theme is that your food choices reflect your individuality and unique needs.
During National Nutrition Month, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics takes center stage by providing a host of healthy eating goals and tips. The 2021 theme is Personalize Your Plate, encouraging people to create a myriad of nutritious meals to meet their own dietary needs and that also align with cultural preferences. The premise of the theme is that your food choices reflect your individuality and unique needs. Even the best-laid healthy eating plan can fall short in important areas. In order to ensure that you are fueling your body with everything that it needs, look into the use of a targeted vitamin/mineral supplement to suit your specific health goals.
Even the best-laid healthy eating plan can fall short in important areas. In order to ensure that you are fueling your body with everything that it needs, look into the use of a targeted vitamin/mineral supplement to suit your specific health goals. Many people erroneously believe that the appearance of their hair and nails is something that they can control with topical solutions. While this is true in some cases, hair and nail symptoms are often simply a sign of some type of internal issue. Because you cannot see these internal issues, it can be challenging to pinpoint why you are suffering from brittle nails, dry hair or other problems.
Many people erroneously believe that the appearance of their hair and nails is something that they can control with topical solutions. While this is true in some cases, hair and nail symptoms are often simply a sign of some type of internal issue. Because you cannot see these internal issues, it can be challenging to pinpoint why you are suffering from brittle nails, dry hair or other problems.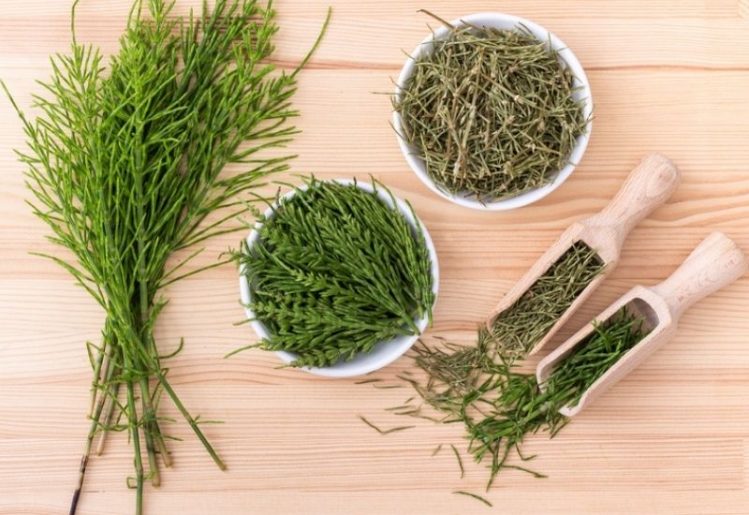 Horsetail is an herb
Horsetail is an herb