A new study from John Hopkins University School of Medicine suggests that Parkinson’s starts in the gut. These recent findings further support the theory that the gut microbiome strongly influences brain health.
Study Finds That Parkinson’s Starts in the Gut
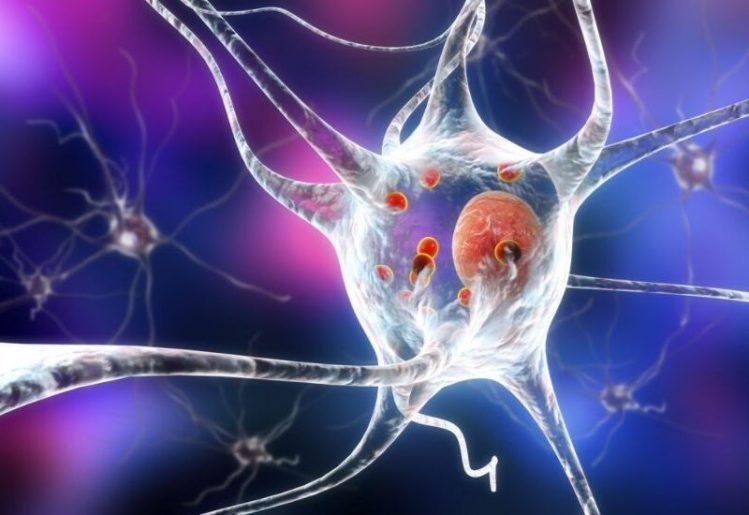 Research conducted recently at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine sought to confirm the theory that Parkinson’s disease first develops in the gut. The study involved injecting small fibrous samples of alpha-synuclein into the guts of test mice and observing how the protein traveled through the system. Once delivered to the brains in humans, alpha-synuclein causes toxic clusters to form, which initiates the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The goal was to see if alpha-synuclein would travel to the brain from the gut.
Research conducted recently at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine sought to confirm the theory that Parkinson’s disease first develops in the gut. The study involved injecting small fibrous samples of alpha-synuclein into the guts of test mice and observing how the protein traveled through the system. Once delivered to the brains in humans, alpha-synuclein causes toxic clusters to form, which initiates the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. The goal was to see if alpha-synuclein would travel to the brain from the gut.
Ted M. Dawson, who co-authored the study, noted that the findings did confirm that the protein traveled to the brain from the gut microbiome. In addition to corroborating the theory that Parkinsons starts in the gut, the research also proved that the disease’s timeline could be tracked. In following the protein’s path, researchers could determine exactly how long it took to travel along the vagus nerve and on to the brain. Since the progression of the protein can be tracked, Mr. Dawson was hopeful that the data could be used to intervene in the development of the disease. Eventually, he hopes a way could be found to stop the protein from reaching the brain, where it causes those toxic clusters to form.
This research follows up a 2003 study that determined that the vagus nerve plays a critical role in carrying alpha-synuclein from the gut microbiome to the brain. It was found that, once the protein found its way to the brain, the clusters it formed inhibited the brain’s normal production of dopamine. Dopamine is a neurotransmitter is essential for proper motor control, mood regulation, concentration and other brain functions that are affected by the development of Parkinson’s disease.
Although the previous study implicated the vagus nerve in transporting alpha-synuclein to the brain, the latest study out of Johns Hopkins was the first animal model and helped researchers track the progression of the disease. It was found that alpha-synuclein took approximately one month to travel from the gut microbiome to the brain stem. Within two more months, the protein had spread to various parts of the brain. It affected the substantia nigra pars compacta, which is the portion of the brain that’s susceptible to Parkinson’s disease, and it also spread to the prefrontal cortex, amygdala and hypothalamus. Eventually the alpha-synuclein spread to the striatum, hippocampus and the olfactory bulb. Essentially, there were very few areas of the brain that were not negatively impacted by the presence of alpha-synuclein.
More Ways the Gut Microbiome Affects Brain Health
While this latest research identifies how Parkinson’s disease originates in the gut microbiome, it’s hardly surprising. We already knew that the gut and brain are connected and can affect one another. This is something we have all experienced even more than we may realize. For example, think about when you’re about to eat and you feel your stomach churning. Upon anticipating food, your brain sends a message to your stomach, which causes the release of digestive acids.
This connection works the other way, as well. An upset stomach can send messages to the brain to give you the symptoms of indigestion, but those types of messages can be sent in the opposite direction as well. This is why people often feel sick to their stomach when experiencing anxiety or a depressive episode.
Another way the connection between the gut and brain is made apparent is in how we react to stress. People tend to think of stress as a purely emotional or mental condition, but it does affect the physical body. Increased stress levels influence the way the gastrointestinal tract functions. By increasing the rate of contraction, stress can cause inflammation to worsen in the gut. If you happen to suffer from a gastrointestinal condition, or an infection, this increased inflammation can send stronger pain signals to the brain. In this way, the brain and gut are interconnected and continuously sending messages back and forth.
Signs That Your Gut Microbiome is Unhealthy
Now that we know the important role that the gut microbiome plays in brain functioning and emotional health, it becomes even more important to look after your gut health. While it can be difficult to know when your gut is unhealthy, paying closer attention to common signs of trouble is important. Recognizing these signs sooner will help you take the steps needed to maintain a healthier gut microbiome, thus improving overall health.
Stomach Problems
 A healthy and diverse gut microbiome is more efficient at digesting your food and flushing waste out of your system. However, when there’s a problem, you’ll experience frequent stomach aches, diarrhea or constipation, heartburn and more frequent gas.
A healthy and diverse gut microbiome is more efficient at digesting your food and flushing waste out of your system. However, when there’s a problem, you’ll experience frequent stomach aches, diarrhea or constipation, heartburn and more frequent gas.
Sugar Cravings
If you eat an unhealthy diet, your gut microbiome won’t be as diverse and it will lack the healthy bacteria your body relies upon. As a result, your body will produce stronger cravings for sugar, which is known to increase inflammation. Feeding this craving will raise your risks of developing disease, including various types of cancer.
Weight Gain
If you’re gaining weight, or unable to lose weight, this may be a sign of a bacterial imbalance in your gut. Certain helpful microbes in the gut microbiome are essential for weight loss, so if you don’t have those types of bacteria, you won’t be able to reach or maintain a healthy weight.
Sleep Disorders
If you’re not getting enough sleep, the problem may be originating in the gut. This is where serotinin is produced and transmitted to the brain, so it can help regulate mood and your ability to sleep.
Even if you don’t recognize any of these symptoms, skin conditions or food allergies may be other indications that there’s an imbalance of bacteria in your gut. The best way to correct the problem is to adopt a healthier plant-based diet. Additionally, taking a high-quality dietary supplement that provides both probiotics and prebiotics can help you correct an imbalance. As you begin making these changes and other lifestyle improvements, you should notice these symptoms going away by themselves.
 When people hear the word “dementia,” most automatically think of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s is indeed one form of dementia, however there are actually many different types. Certain symptoms are common to most types of dementia. While memory loss is a typical symptom, experiencing memory problems can be the result of any number of medical conditions. Only when memory loss is one of many cognitive impairment symptoms does it indicate the possibility of dementia.
When people hear the word “dementia,” most automatically think of Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s is indeed one form of dementia, however there are actually many different types. Certain symptoms are common to most types of dementia. While memory loss is a typical symptom, experiencing memory problems can be the result of any number of medical conditions. Only when memory loss is one of many cognitive impairment symptoms does it indicate the possibility of dementia. Like St. John’s Wort, S-adenosylmethionine, or SAMe, hasn’t been approved to treat depression. Although more clinical research is needed, some people do find that it helps elevate the mood. People with bipolar disorder should use the supplement with caution because it can trigger manic episodes.
Like St. John’s Wort, S-adenosylmethionine, or SAMe, hasn’t been approved to treat depression. Although more clinical research is needed, some people do find that it helps elevate the mood. People with bipolar disorder should use the supplement with caution because it can trigger manic episodes. Autism affects one out of every 59 children born in the United States, and is more common in boys than in girls. A look at past statistics shows that incidences of autism have nearly doubled over the past 14 years. If your child has autism, you already know that the condition affects their ability to interact with others. It can be hard to identify in some children, because it can affect each person differently. Autism may not be curable as of yet, but it can be treated. To obtain the best results from treatment, it’s important to begin as soon as possible. This means being able to recognize the signs and symptoms of autism, such as:
Autism affects one out of every 59 children born in the United States, and is more common in boys than in girls. A look at past statistics shows that incidences of autism have nearly doubled over the past 14 years. If your child has autism, you already know that the condition affects their ability to interact with others. It can be hard to identify in some children, because it can affect each person differently. Autism may not be curable as of yet, but it can be treated. To obtain the best results from treatment, it’s important to begin as soon as possible. This means being able to recognize the signs and symptoms of autism, such as: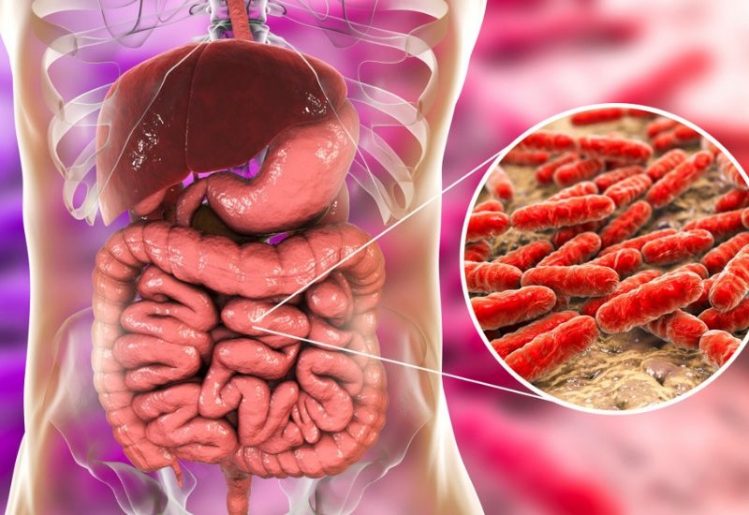 New research has found a link between gut bacteria and autism. The findings were the result of a research project intending to see if the common gastrointestinal problems experienced by most autistic children could be treated. Researchers at Arizona State University hoped to alleviate gastrointestinal problems experienced by
New research has found a link between gut bacteria and autism. The findings were the result of a research project intending to see if the common gastrointestinal problems experienced by most autistic children could be treated. Researchers at Arizona State University hoped to alleviate gastrointestinal problems experienced by  We have known for several decades that schizophrenia is the result of a chemical imbalance in the brain. We also know that glutamate is involved in the development of schizophrenia and that the enzyme is present in glutathione. When studying the levels of these enzymes in the various parts of the brain, researchers have found that schizophrenia patients had lower glutathione levels in the anterior cingulate cortex and thalamus. There was an average of three percent less glutathione in the anterior cingulate cortex, while there was an eight-percent lower level of the enzyme in the thalamus of the brain.
We have known for several decades that schizophrenia is the result of a chemical imbalance in the brain. We also know that glutamate is involved in the development of schizophrenia and that the enzyme is present in glutathione. When studying the levels of these enzymes in the various parts of the brain, researchers have found that schizophrenia patients had lower glutathione levels in the anterior cingulate cortex and thalamus. There was an average of three percent less glutathione in the anterior cingulate cortex, while there was an eight-percent lower level of the enzyme in the thalamus of the brain. A University of East Anglia research team has announced that they’re ready to begin human trials on a possible new
A University of East Anglia research team has announced that they’re ready to begin human trials on a possible new  In a world where obesity and associated diseases are becoming serious public health hazards, there is a great deal of advice being offered when it comes to weight loss and general health. Cutting back on meats — or cutting them out altogether — is one commonly repeated suggestion. However, new research suggests that this may not be the best advice.
In a world where obesity and associated diseases are becoming serious public health hazards, there is a great deal of advice being offered when it comes to weight loss and general health. Cutting back on meats — or cutting them out altogether — is one commonly repeated suggestion. However, new research suggests that this may not be the best advice. Although it is important to eat a wide range of plant-based foods, eating meat and other animal products may be just as important to human health. We need certain nutrients that only animal foods can provide. Although vegetarian diets can provide similar oils, the ones that come from animals and seafood are far different and play a very different role in our bodies. Omega-3 acids derived from plant sources have
Although it is important to eat a wide range of plant-based foods, eating meat and other animal products may be just as important to human health. We need certain nutrients that only animal foods can provide. Although vegetarian diets can provide similar oils, the ones that come from animals and seafood are far different and play a very different role in our bodies. Omega-3 acids derived from plant sources have  Each condition included in the overall category of neurocognitive disorders is characterized by its own unique set of symptoms. However, there are some symptoms that are common among most of these disorders. In general, any form of cognitive decline may involve the following symptoms:
Each condition included in the overall category of neurocognitive disorders is characterized by its own unique set of symptoms. However, there are some symptoms that are common among most of these disorders. In general, any form of cognitive decline may involve the following symptoms: While the study uncovered 72 cases of neurocognitive disorders, the overall assessment concluded that drinking tea did have a positive effect on cognitive decline. When compared to individuals who did not regularly consume green or black tea, the tea drinkers exhibited a reduced risk of developing cognitive decline. The researchers also found that female tea drinkers exhibited a greater reduction in risk of neurocognitive disorders than male tea drinkers.
While the study uncovered 72 cases of neurocognitive disorders, the overall assessment concluded that drinking tea did have a positive effect on cognitive decline. When compared to individuals who did not regularly consume green or black tea, the tea drinkers exhibited a reduced risk of developing cognitive decline. The researchers also found that female tea drinkers exhibited a greater reduction in risk of neurocognitive disorders than male tea drinkers.