After more than a century of study, science is making real breakthroughs in its understanding of how nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) works in cells to preserve cellular health and function, as well as fight disease. First discovered in 1906 through a study on the fermentation of yeast, modern science recognizes that NAD is present in all living cells as an essential coenzyme with a vital role in aiding the cells’ mitochondria to produce energy. NAD affects the body on a cellular level, impacting mitochondrial performance. Learn more about how anti-aging nutrient NADH benefits include helping to fight disease and protect overall health.
What NAD Does
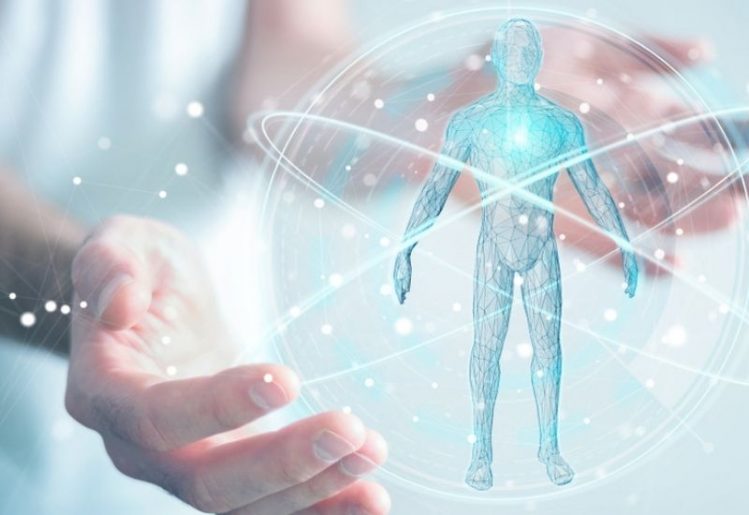 NAD takes two forms, depending on what point in the energy production cycle it is. These two forms are NAD+ and NADH. NAD levels decrease with age, contributing to the mitochondrial inefficiency and deterioration linked to aging and disease processes.
NAD takes two forms, depending on what point in the energy production cycle it is. These two forms are NAD+ and NADH. NAD levels decrease with age, contributing to the mitochondrial inefficiency and deterioration linked to aging and disease processes.
The human body is made up of an amazingly complex set of highly integrated systems that act as a whole. The foundation of all body and mind functions lies in the almost inconceivable number of chemical reactions and electrical impulses that take place in our cells, molecules, atoms and subatomic particles. As an essential coenzyme, NAD acts as a critical partner, or helper molecule, to regulating proteins, called enzymes, facilitating and enabling the chemical reactions that form the base of the life processes and functions of cells. NAD is essential to the processes involved in the generation of energy by the mitochondria due to its dual function of receiving and providing electrons.
Understanding the Forms NAD Takes
NAD is a term used to encompass the two forms it takes (NAD+ and NADH) while giving or receiving electrons during energy production and transfer processes. When NAD is oxidized, it becomes NAD+, with one of its nitrogen atoms having a positive charge. NAD+, in its role in breaking down glucose into usable elements, receives the electrons and hydrogen produced by that metabolic process. The breaking down of glucose involves chemical reactions called redox reactions.
In its coenzyme role, NAD+ has been linked to the function and health of the mitochondria and sirtuins, which help regulate cellular metabolism and a cell’s response to various types of cellular stress, including oxidative stress. Sirtuins have been linked to the aging process and longevity, as well as some disease processes, including many of those related to the metabolic system and inflammation.
When NAD+ receives hydrogen and two electrons, it shifts into its high energy form, NADH. This is the NAD form that transports and donates electrons, giving it a critical role in energy production. After donating its electrons, eventually NADH is converted to NAD+ again. During the glucose metabolism process, each molecule of glucose yields two NADH molecules. The ratio of NAD+ to NADH tends to skew toward NADH because NAD+ levels go down as we get older. Science has not yet confirmed the ideal ratio between the two, but do theorize that disruptions of that ratio can contribute to aging and disease processes.
How NADH Benefits Health and Well-Being
NAD, via its two forms – NAD+ and NADH – impact health and well-being in a variety of ways. The role of NAD in metabolizing glucose and receiving, transporting and donating electrons is critical to life itself. However, its role in health extends well beyond that vital function. NAD+ and NAHD benefits have been getting a lot of attention from scientists specializing in anti-aging and aging-related disease prevention. That’s not surprising considering the connection between mitochondrial deterioration and aging.
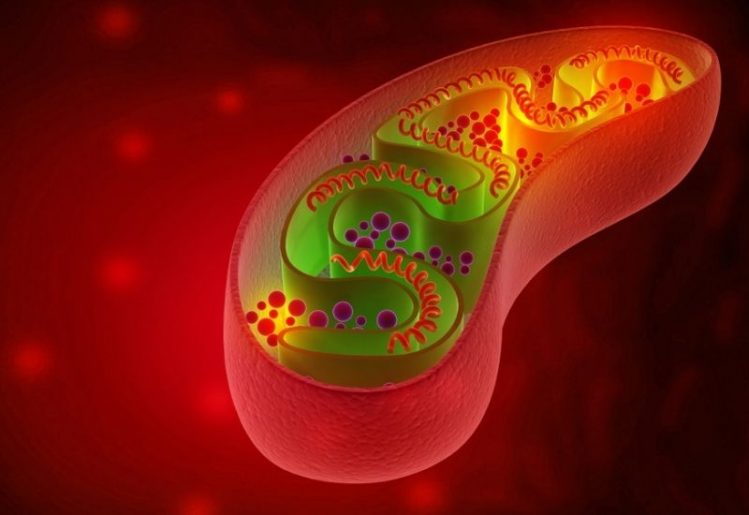 In animal studies and test tube studies done with human muscle tissue, increasing NAD+ has been shown to improve age-weakened muscles. This is thought to relate to the impact of the increased NAD+ and NADH on mitochondrial health. Studies have connected the use of NAD supplements to a number of health benefits relating to the role of this substance in mitochondrial energy production.
In animal studies and test tube studies done with human muscle tissue, increasing NAD+ has been shown to improve age-weakened muscles. This is thought to relate to the impact of the increased NAD+ and NADH on mitochondrial health. Studies have connected the use of NAD supplements to a number of health benefits relating to the role of this substance in mitochondrial energy production.
These NADH benefits include better cognitive performance, improved circadian rhythm regulation, reduced fatigue, decrease in symptoms in those suffering from chronic fatigue syndrome, healthier skin and protection against age-related vision problems. Some studies show a link between NAD+ levels and better cardiovascular health.
NAD has a vital role in many essential processes that protect health and well-being. Among these are DNA repair, oxidative stress mitigation on a cellular level and metabolic efficiency. As the body of information grows concerning the function of NAD+ and NADH, scientists are looking at how to translate this new information into effective treatments for such diseases as Alzheimer’s and dementia, as well as developing effective strategies to protect against the diseases and physical frailties associated with aging.
New Knowledge Builds Upon Old
While much of the newest knowledge concerning NAD+ and NADH benefits is based on animal studies, it is built upon a foundation of older knowledge that goes back more than 100 years. This value of this vital coenzyme has long been recognized for its critical role in overall health and well-being.
Vital to cellular energy and function, NAD+ and NADH support health at the most foundational levels. NAD supports DNA health and function, the energy producing metabolic system and is firmly linked to the aging process via its coenzyme action in relation to sirtuins. If you choose to use supplements to boost NAD+, do your research and choose a high-quality, fully bioavailable supplement.
 In its most basic definition, melatonin is a hormone produced by the body’s pineal gland. The
In its most basic definition, melatonin is a hormone produced by the body’s pineal gland. The  In order to boost production of melatonin in the evening, you need to increase the levels of serotonin in the morning. You can support serotonin production by exposing your body to sunlight in the morning.
In order to boost production of melatonin in the evening, you need to increase the levels of serotonin in the morning. You can support serotonin production by exposing your body to sunlight in the morning.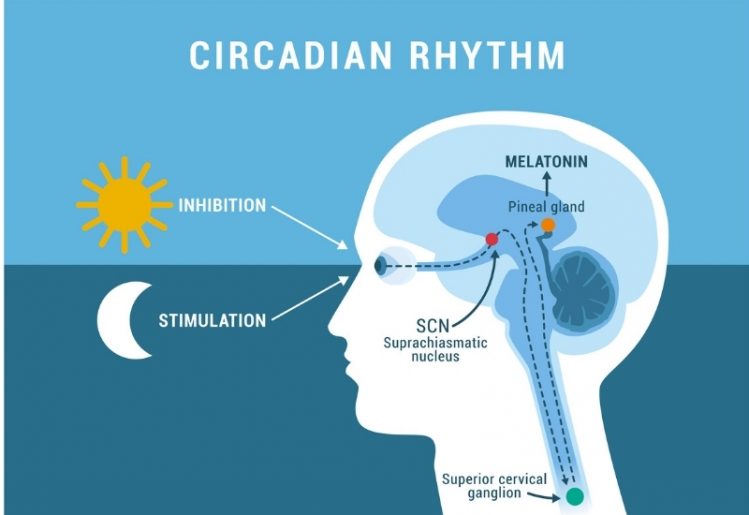 While
While  Instead of using your electronic device, create a relaxation ritual that you can do every night. This will help you train your brain to recognize the signs that it’s time for rest, while also helping you wind down. This can involve taking a warm bath, reading a good book or meditating to soft music. Any practice that you find relaxing and enjoyable can be included in your bedtime ritual.
Instead of using your electronic device, create a relaxation ritual that you can do every night. This will help you train your brain to recognize the signs that it’s time for rest, while also helping you wind down. This can involve taking a warm bath, reading a good book or meditating to soft music. Any practice that you find relaxing and enjoyable can be included in your bedtime ritual. While setting the stage for slumber is one role of melatonin, it does much more than just help people fall asleep. Even after you fall asleep, melatonin acts as a powerful antioxidant, assisting the body in maintaining health and repairing damage throughout the night.
While setting the stage for slumber is one role of melatonin, it does much more than just help people fall asleep. Even after you fall asleep, melatonin acts as a powerful antioxidant, assisting the body in maintaining health and repairing damage throughout the night. If you spend the majority of your day indoors, you may be inhibiting the way your circadian rhythm functions. By spending some time outside, where you can benefit from direct sunlight exposure, you’ll be helping your brain adjust to the 24 -hour cycle. Getting that sunlight earlier in the day will help kick start the production of melatonin earlier in the evening.
If you spend the majority of your day indoors, you may be inhibiting the way your circadian rhythm functions. By spending some time outside, where you can benefit from direct sunlight exposure, you’ll be helping your brain adjust to the 24 -hour cycle. Getting that sunlight earlier in the day will help kick start the production of melatonin earlier in the evening. There is a confirmed link between melatonin and metabolism; but how does a hormone that promotes sleep also help the body burn fat? In a
There is a confirmed link between melatonin and metabolism; but how does a hormone that promotes sleep also help the body burn fat? In a  It’s just as important to expose yourself to natural sunlight as much as possible during the morning and early afternoon hours. If you’re not getting this sunlight exposure, your circadian rhythm can be thrown off balance and may not produce
It’s just as important to expose yourself to natural sunlight as much as possible during the morning and early afternoon hours. If you’re not getting this sunlight exposure, your circadian rhythm can be thrown off balance and may not produce  Most people know that they’re more likely to get sick when they’re not well rested, but research into this area has uncovered
Most people know that they’re more likely to get sick when they’re not well rested, but research into this area has uncovered  Your environment is just as important as your bedding when it comes to creating a sleep-friendly atmosphere. If you notice excess lighting spilling into your bedroom from a window or from the corridor, it may be helpful to wear a sleep mask. Similarly, wearing earplugs, or noise-canceling earmuffs, to bed can keep noises from waking you in the night.
Your environment is just as important as your bedding when it comes to creating a sleep-friendly atmosphere. If you notice excess lighting spilling into your bedroom from a window or from the corridor, it may be helpful to wear a sleep mask. Similarly, wearing earplugs, or noise-canceling earmuffs, to bed can keep noises from waking you in the night.