Vitamin D is a crucial fat-soluble vitamin that plays multiple roles in ensuring overall health and wellness. Vitamin D is naturally present in a few types of foods, but can also be obtained from a supplement or most famously, via sun exposure. If you are not getting a sufficient amount of vitamin D, you are putting your personal health at risk. This guide to vitamin D is intended to help empower you to make smart decisions about your food choices, supplements and sun exposure.
Why is Vitamin D Important?
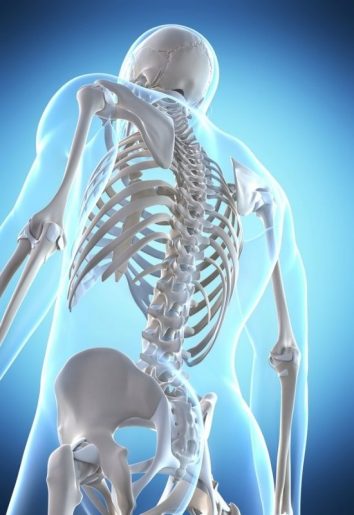 Vitamin D is most useful in supporting calcium absorption throughout the body, particularly in the gut. Vitamin D also works in tandem with calcium for bone growth and maintenance. The bones in the body are more likely to become too thin and brittle without adequate levels of vitamin D. Sufficient levels of vitamin D in children will help to prevent rickets. For adults, vitamin D, along with calcium, is needed to mitigate the risk of developing osteoporosis. Inadequate vitamin D levels are also associated with a variety of other health issues, including poorer colorectal cancer outcomes, joint pain, periodontal disease, decreased muscle strength and more.
Vitamin D is most useful in supporting calcium absorption throughout the body, particularly in the gut. Vitamin D also works in tandem with calcium for bone growth and maintenance. The bones in the body are more likely to become too thin and brittle without adequate levels of vitamin D. Sufficient levels of vitamin D in children will help to prevent rickets. For adults, vitamin D, along with calcium, is needed to mitigate the risk of developing osteoporosis. Inadequate vitamin D levels are also associated with a variety of other health issues, including poorer colorectal cancer outcomes, joint pain, periodontal disease, decreased muscle strength and more.
Signs You May be Low on Vitamin D
There are a number of symptoms that may present if you are low on vitamin D. Because this vitamin is so important for bone and muscle strength, a general feeling of weakness is associated with a vitamin D deficiency. Increased incidences of depression, fatigue and mood swings also may be signs that you are not getting enough of this crucial vitamin.
Other signs that you may be deficient in vitamin D include high blood pressure, hair loss, a depressed immune system, a greater sensitivity to pain, chronic gum disease, problems with your gut and greater susceptibility to allergies.
In addition to these short-term health issues, a vitamin D deficiency that continues for the long-term can lead to a host of chronic complications. This includes an increased risk for developing cancer, autoimmune issues, type II diabetes, cardiovascular problems, pregnancy complications and more.
The bottom line is that there are a variety of health conditions that you may be at a higher risk of developing both in the short-term and in the long-term if you are not diligent about getting enough of this important vitamin.
How to Ensure You Are Getting Enough Vitamin D
Now that you know about the problems associated with a deficiency in vitamin D, you are probably wondering how you can ensure that you are taking in enough of this crucial nutrient. Here are the three primary ways to boost your intake of vitamin D.
Food
While vitamin D is not plentiful in a wide variety of foods, it is still possible to boost your intake by focusing on foods that feature the nutrient. Good food sources for vitamin D include cheese, fatty fish, mushrooms, egg yolks and beef liver. You can also find many foods that are fortified with vitamin D. The most common foods that are fortified with vitamin D include cereal, bread, milk and orange juice.
Sun
You may have heard the phrase, “soaking up that vitamin D.” This is because the sun is one of the best sources of vitamin D. The sun’s rays hitting the body’s bare skin stimulates the production of vitamin D. Because the UVB radiation does not travel through glass, sun exposure needs to be direct. You will receive the highest concentration of vitamin D if you spend time in the sunlight between the hours of 10 a.m. and 4 p.m..
Supplements
If you are worried that you are not getting enough vitamin D, you may want to consider the use of supplements as an added layer of insurance. There are a number of highly effective supplements that provide vitamin D, including Vitachron.
The Great Sunscreen Debate
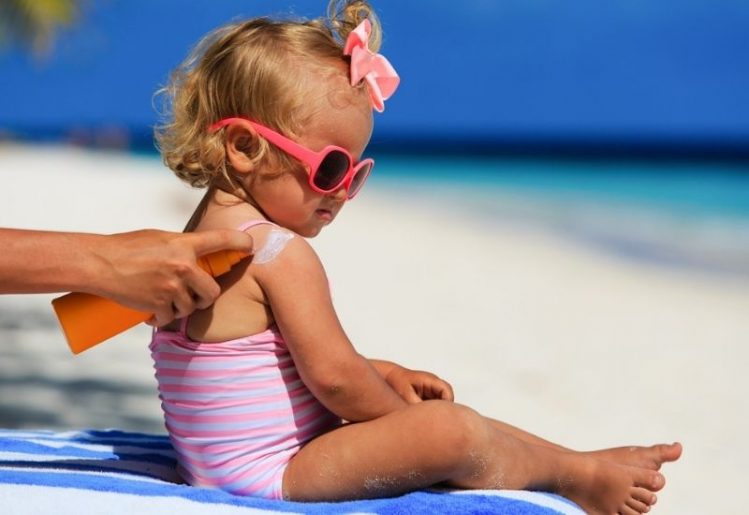 Because vitamin D is not as plentiful in foods as other vitamins, many people turn to the sun to deliver this nutrient. The challenge is finding that balance between sufficient protection from the sun and getting your daily dose of vitamin D.
Because vitamin D is not as plentiful in foods as other vitamins, many people turn to the sun to deliver this nutrient. The challenge is finding that balance between sufficient protection from the sun and getting your daily dose of vitamin D.
As more is understood about vitamin D, the great sunscreen debate continues to rage on. Practicing sensible sun-protective measures is the best way to protect yourself against skin cancer while also ensuring that you are getting enough vitamin D. This means that you should avoid applying sunscreen so thickly that it blocks out all of the sun’s ability to provide vitamin D. It is also important to remember that most people only need about 20 minutes of sun exposure a few times per week to generate the amount of vitamin D needed for optimal health.
When it comes to vitamin D exposure via the sun, keep in mind that a little goes a long way. You do not need to bake in the sun to see the benefits.
Understanding the importance of vitamin D and how you can guarantee that you are taking in adequate amounts can have a profound positive effect on your overall health and well-being.
 There are many ways vitamin B12 benefits everyone, regardless of age and gender. We know that vitamin B12 helps the body form new red blood cells and improves the metabolism of cells throughout the body. It also benefits nerve function and helps the body create new DNA. Vitamin B12 also promotes a healthy heart and helps to maintain blood pressure within normal ranges
There are many ways vitamin B12 benefits everyone, regardless of age and gender. We know that vitamin B12 helps the body form new red blood cells and improves the metabolism of cells throughout the body. It also benefits nerve function and helps the body create new DNA. Vitamin B12 also promotes a healthy heart and helps to maintain blood pressure within normal ranges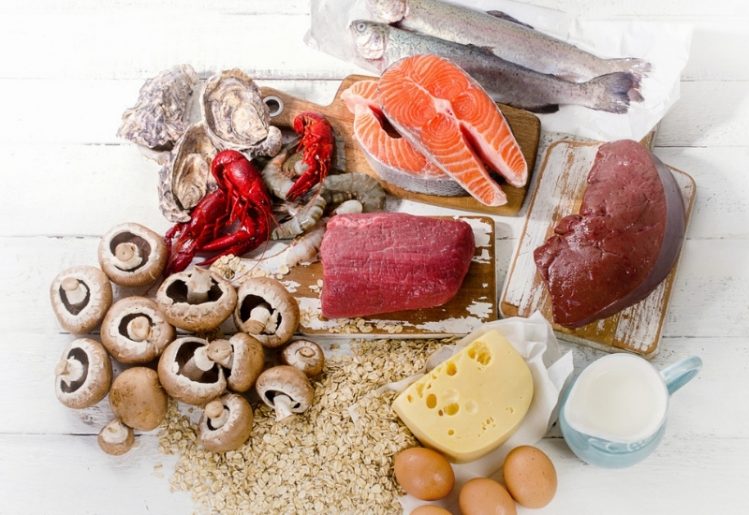  While organ meat from any animal is packed with a broad range of nutrients, the liver and kidneys of a lamb are particularly rich in vitamin B12, containing 3,571 percent of the daily recommended value, making it ideal for pregnant women. Lamb organ meat is also rich in vitamin A, vitamin B2, selenium and copper.
While organ meat from any animal is packed with a broad range of nutrients, the liver and kidneys of a lamb are particularly rich in vitamin B12, containing 3,571 percent of the daily recommended value, making it ideal for pregnant women. Lamb organ meat is also rich in vitamin A, vitamin B2, selenium and copper.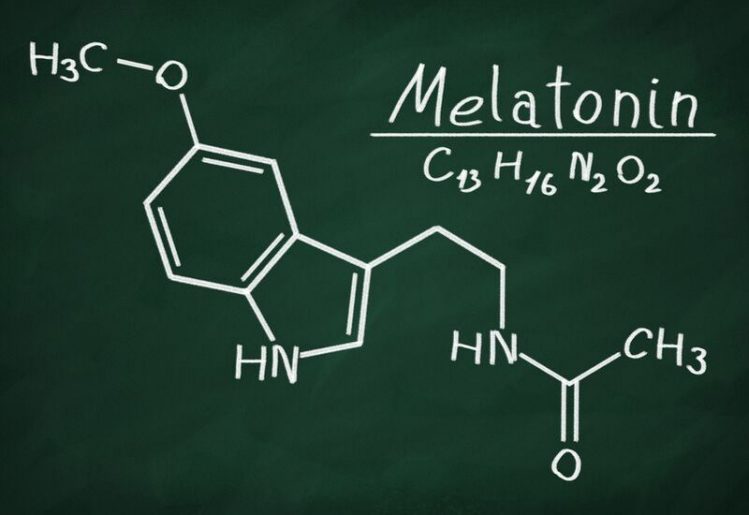 Because pregnancy is so common — after all, it is how we all got here — we forget that it is a complex physiological process that relies on an intricate cascade of hormones and growth factors. According to some studies, melatonin appears to play an important role. Fetuses begin to make melatonin very late in the pregnancy, and even then will not make sufficient amounts until several months after birth. Instead, they rely on melatonin made by their mothers, which appears to cross the placental barrier easily.
Because pregnancy is so common — after all, it is how we all got here — we forget that it is a complex physiological process that relies on an intricate cascade of hormones and growth factors. According to some studies, melatonin appears to play an important role. Fetuses begin to make melatonin very late in the pregnancy, and even then will not make sufficient amounts until several months after birth. Instead, they rely on melatonin made by their mothers, which appears to cross the placental barrier easily. Many of the studies looking at the long term effects of melatonin were performed on mice, rats and other animals due to the understandable restrictions on experimenting on human infants and fetuses. However, melatonin appears to act in the same manner in all mammals, suggesting that it may have similar effects on human babies. Because melatonin has relatively few side effects, supplementation may be a safe way to give a pregnancy the best possible chance.
Many of the studies looking at the long term effects of melatonin were performed on mice, rats and other animals due to the understandable restrictions on experimenting on human infants and fetuses. However, melatonin appears to act in the same manner in all mammals, suggesting that it may have similar effects on human babies. Because melatonin has relatively few side effects, supplementation may be a safe way to give a pregnancy the best possible chance. With the number of obese people on the rise around the globe and the prevalence of dementia expected to increase to upwards of 80 million by the year 2040, these findings could have “significant implications” for many. Senior study author Conal Cunningham, an associate professor at Trinity College said in a
With the number of obese people on the rise around the globe and the prevalence of dementia expected to increase to upwards of 80 million by the year 2040, these findings could have “significant implications” for many. Senior study author Conal Cunningham, an associate professor at Trinity College said in a  According to a new study in Sweden, women who take vitamins and supplements during pregnancy have a
According to a new study in Sweden, women who take vitamins and supplements during pregnancy have a  Omega-3 fatty acids have been previously found to be important in the brain health of adults, slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases and providing a wide variety of cognitive benefit. They appear to be especially important to the rapidly growing brain of a fetus. However, this study is not the only link between maternal diet and schizophrenia. Another recent study found that
Omega-3 fatty acids have been previously found to be important in the brain health of adults, slowing the progression of neurodegenerative diseases and providing a wide variety of cognitive benefit. They appear to be especially important to the rapidly growing brain of a fetus. However, this study is not the only link between maternal diet and schizophrenia. Another recent study found that