One of the most common parenting struggles occurs at the kitchen table. While most parents want their children to eat a healthy variety of foods, many children are picky eaters who make this a challenge. Introducing a variety of healthy foods is both time-consuming and expensive for many families. However, research suggests that nutrition is essential to both physical and mental health, and according to a new study, eating fish weekly may even make children smarter and help them to sleep better.
The Health Benefits of Fish
 Aside from the health benefits of fish, people in the Western world are eating less of it than in prior generations. Although modern food storage and transportation have made seafood available even in inland areas, fish is expensive and requires care in both storage and preparation. Many people also have concerns about pollutants such as mercury that are present in certain types of seafood. Last, there are environmental concerns as over-fishing has compromised certain ecosystems. Even with these concerns, experts recommend that people eat fish in moderate amounts.
Aside from the health benefits of fish, people in the Western world are eating less of it than in prior generations. Although modern food storage and transportation have made seafood available even in inland areas, fish is expensive and requires care in both storage and preparation. Many people also have concerns about pollutants such as mercury that are present in certain types of seafood. Last, there are environmental concerns as over-fishing has compromised certain ecosystems. Even with these concerns, experts recommend that people eat fish in moderate amounts.
Limited seafood consumption decreases pollutant exposure and environmental impact, yet provides beneficial nutrients that would otherwise be lacking if it was avoided entirely. There are health benefits from fish that are difficult to get from other foods. Fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids and other long chain fatty acids with proven positive effects. In addition, fish are a rich source of lean protein as well as several essential vitamins. Eating fish in moderation can improve one’s health immensely, and, as previously mentioned, eating fish weekly can especially benefit children.
Could Eating Fish Weekly Make Kids Smarter?
Everyone wants to give their children the best possible start in life, and existing research has suggested that there are several ways to do this. In particular, early child education, reading to children and supplementing their diet with long chain fatty acids (such as those found in fish) appear to have a measurable impact. Children who have these three factors consistently score higher on intelligence quotient (IQ) tests. Eating fish weekly also appears to improve children’s sleep, which in turn improves health and academic performance.
However, prior research has been slightly controversial for several reasons. Although it showed a link between eating seafood, high intelligence and better sleep, there were possible confounding factors. People who can afford fish, for example, may be more likely to be able to afford high-quality preschools and other things that improve intelligence. A new study has addressed these objections by looking solely at the effects of eating fish weekly on intelligence and sleep, with other factors accounted for.
New Links Between Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Sleep and Intelligence
Researchers looked at more than 500 children in China. Parents were asked about the children’s diet, particularly how often they ate fish. In addition, children underwent an intelligence test and evaluation of their sleeping habits. Finally, researchers controlled for parental education, family size and other factors that are purported to affect both intelligence and sleep. The results of this analysis showed a statistically significant link between eating fish, sleep quality and intelligence, even among children who otherwise had similar backgrounds and advantages.
How much of a difference can eating fish weekly make in a child’s life? Children who ate fish on a weekly basis had an average IQ that was 4.8 points higher than those who reported eating it rarely or never. Eating fish even occasionally raised IQ by 3.3 points. Eating fish weekly also was linked to a lower rate of sleep disturbances. Although this study did not look specifically at omega-3 fatty acids, these compounds are believed to be the reason for the improvements in sleep and intelligence.
A Healthy Diet for a Healthy Start
 The evidence is clear that diet and other lifestyle factors can have a sizable impact on pediatric health. However, many parents struggle to help their children eat right. Many children have a natural preference for salty and sugary foods. In addition, many initially dislike the strong flavors of healthy foods such as fish and vegetables. However, the effort will likely pay off in better long-term health. There are a few ways that parents can encourage a healthy diet and teach children good habits for a lifetime:
The evidence is clear that diet and other lifestyle factors can have a sizable impact on pediatric health. However, many parents struggle to help their children eat right. Many children have a natural preference for salty and sugary foods. In addition, many initially dislike the strong flavors of healthy foods such as fish and vegetables. However, the effort will likely pay off in better long-term health. There are a few ways that parents can encourage a healthy diet and teach children good habits for a lifetime:
- Keep only healthy options in your home. Children will eat healthy foods when these are the only foods available.
- Encourage children to enjoy treats in moderation rather than banning them altogether or restricting them excessively.
- Praise healthy food choices rather than criticizing poor ones. Children, like all people, respond best to positive reinforcement.
- Eat together. This allows children to see adults modeling healthy choices.
- Do not force or pressure to eat. They will make healthy choices if these are the only ones available. Force will make them dislike healthy foods.
- Give children control. Let them select foods at the store and request dishes they enjoy.
- Supplement with an omega-3 fatty acid supplement if they show a long-term aversion to seafood.
Diet and nutrition appear to be important in a child’s lifelong health, intelligence and sleep quality. Although teaching them to eat healthy can be a challenge, it will lay the foundation for a lifetime of good choices and improved well-being.
 Most people have experienced burn out to some degree, either in themselves or in coworkers. You begin to take less pride in your work and express cynical attitudes. Some people begin to depersonalize others, caring less about the person’s feelings and acting without consideration. Although everyone feels burned out at times, it is merely a short phase for most of us.
Most people have experienced burn out to some degree, either in themselves or in coworkers. You begin to take less pride in your work and express cynical attitudes. Some people begin to depersonalize others, caring less about the person’s feelings and acting without consideration. Although everyone feels burned out at times, it is merely a short phase for most of us. Are you suffering from burnout? Here are
Are you suffering from burnout? Here are  There are several factors that contribute to depression in the darker months of the year (the causes of summertime depression are much less understood). Serotonin is a neurotransmitter highly responsible for maintaining a normal mood; production of this chemical is partly triggered by sunlight exposure. Since there is much less sunlight during the fall and winter, serotonin levels can plummet. Less sunlight also means less
There are several factors that contribute to depression in the darker months of the year (the causes of summertime depression are much less understood). Serotonin is a neurotransmitter highly responsible for maintaining a normal mood; production of this chemical is partly triggered by sunlight exposure. Since there is much less sunlight during the fall and winter, serotonin levels can plummet. Less sunlight also means less 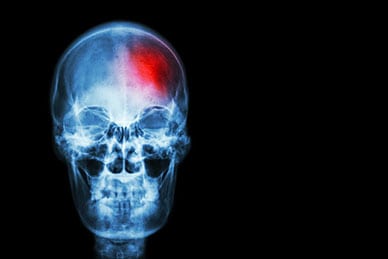 The study involved collecting information about 40 adults who had suffered a hemorrhagic stroke and who had been admitted to the Intensive Care Unit within 24 hours of the event. The researchers had some of the patients receive 30 milligrams of
The study involved collecting information about 40 adults who had suffered a hemorrhagic stroke and who had been admitted to the Intensive Care Unit within 24 hours of the event. The researchers had some of the patients receive 30 milligrams of  All living creatures have
All living creatures have  While we now understand more about the circadian rhythm than we ever have, modern life makes maintaining a stable internal clock a greater challenge than ever before. People are working increasingly erratic hours due to a planet where the business day never stops. Many people work odd shifts that keep them from waking and going to bed at a regular time. Travel for work and personal reasons has made jet lag a common affliction. Even simple things like daylight savings time can throw internal clocks off kilter.
While we now understand more about the circadian rhythm than we ever have, modern life makes maintaining a stable internal clock a greater challenge than ever before. People are working increasingly erratic hours due to a planet where the business day never stops. Many people work odd shifts that keep them from waking and going to bed at a regular time. Travel for work and personal reasons has made jet lag a common affliction. Even simple things like daylight savings time can throw internal clocks off kilter. Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain. While there are small amounts of melatonin found in some foods like vegetables and meat, it’s most commonly used in supplement form.
Melatonin is a hormone produced by the pineal gland in the brain. While there are small amounts of melatonin found in some foods like vegetables and meat, it’s most commonly used in supplement form. Combining sedatives may result in excessive drowsiness or loss of consciousness, but some people experience the opposite effect. Some people feel like they have taken a stimulant when alcohol is combined with melatonin. This may be due to the body reacting to alcohol by producing adrenaline.
Combining sedatives may result in excessive drowsiness or loss of consciousness, but some people experience the opposite effect. Some people feel like they have taken a stimulant when alcohol is combined with melatonin. This may be due to the body reacting to alcohol by producing adrenaline.