Serotonin (also referred to as 5-hydroxytryptamine or 5-HT) is a chemical messenger that helps the nerve cells in the body communicate. While serotonin was discovered by scientists over 60 years ago, the study of its importance to healthy body function continues to evolve. A serotonin deficiency has been linked to a variety of physical and mental health issues, making it important that you recognize and treat the problem. Here are a few things to know about this neurotransmitter that may help shed light on potential health issues as well as ideas on how you can boost serotonin levels naturally.
Why is Serotonin Important to Overall Well-being?
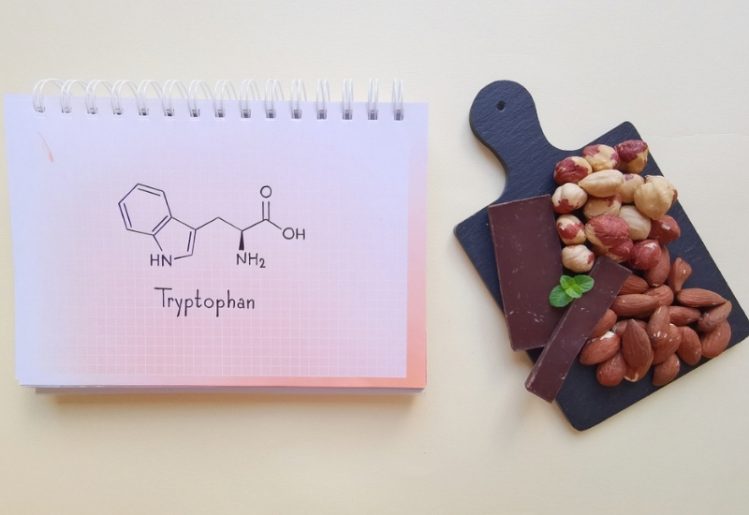 Your body produces serotonin from the essential amino acid tryptophan. The body sends signals between nerve cells through this vital neurotransmitter. While serotonin is primarily found in the digestive system, it is also present in various areas of the central nervous system, such as the brain, as well in blood platelets.
Your body produces serotonin from the essential amino acid tryptophan. The body sends signals between nerve cells through this vital neurotransmitter. While serotonin is primarily found in the digestive system, it is also present in various areas of the central nervous system, such as the brain, as well in blood platelets.
Getting adequate amounts of nutrients like tryptophan, vitamin D, omega-3 fatty acids and certain B vitamins is necessary for your body to produce adequate levels of serotonin. Tryptophan is especially important when it comes to serotonin production. Without enough tryptophan in your diet, you may experience lower-than-desired levels of serotonin.
Serotonin is instrumental in a variety of bodily functions. This chemical modulates almost every behavioral function in the human body, including mood, aggression, memory, appetite, sexual function, anger and more. This means that serotonin plays a critical role in achieving adequate amounts of sleep, enjoying a positive mindset, experiencing good digestive support, having a rewarding sex life and much more. In fact, it is easier to find something that serotonin does not have a hand in than to try to list all of the functions that it touches.
What Causes Serotonin Deficiency?
There are a number of factors that may lead to a deficiency in serotonin. Because serotonin comes from tryptophan, a deficiency in this amino acid may cause serotonin levels to drop below an acceptable level. When a deficiency is present, it can be difficult to ascertain what is causing it precisely because serotonin has so many functions.
Scientists know that some of the most common causes of seroconin deficiency include changes in the brain related to age, not eating the right mix of healthy foods, chronic stress, poor exercise habits and inadequate amounts of natural light exposure. While it is possible to test serotonin levels, most physicians will try to evaluate possible conditions related to low levels of the neurotransmitter.
What Are the Symptoms of Serotonin Deficiency?
Low levels of serotonin can manifest through both physical and mental health issues. Some of the most common physical symptoms that may indicate a deficiency in this crucial chemical include problems with movement or balance, sexual issues as such as premature ejaculation and difficulties with digestion and incontinence. Individuals with low serotonin may also experience problems with wound healing because of poor blood clotting ability as well as unexplained chronic pain.
Low serotonin levels may also present through mental health problems. Some of the most common indicators of this deficiency include unexplained depression or anxiety, issues with memory or concentration and schizophrenia. Because serotonin helps to regulate sleep patterns, you may have problems falling or staying asleep if you are low on this neurotransmitter. Other symptoms of a deficiency include hyperactivity and issues related to sexual function such as changes in desire and the ability to find pleasure in sexual activity.
How to Boost Serotonin Levels Naturally
The good news is that there are many things that you can do to boost your serotonin levels naturally. Here are just a few ideas to consider if you or your doctor suspect serotonin deficiency.
Seek Out Natural Light
In addition to treating various types of seasonal depression, exposing yourself to natural light can help to boost serotonin levels. If this is a challenge for you because of your climate or lifestyle, you may want to consider using a light therapy lamp.
Focus on Emotional Well-being
Because serotonin levels and mental health are linked, it is recommended that you make your emotional well-being a priority. You can do this by being diligent about reducing chronic levels of stress in your life. Some people also find success in boosting serotonin through the use of psychotherapy. Engaging in these types of cognitive or behavioral therapies can have a positive effect on serotonin levels so that you feel better emotionally.
Get Moving
 As with many health conditions, a little exercise can go a long way in helping to combat a myriad of issues. Regular exercise has been shown to raise serotonin levels, giving you just one more reason to commit to a consistent routine.
As with many health conditions, a little exercise can go a long way in helping to combat a myriad of issues. Regular exercise has been shown to raise serotonin levels, giving you just one more reason to commit to a consistent routine.
Watch Your Diet
Focusing on good nutrition can play a pivotal role in encouraging the production of serotonin. In addition to general nutritional guidelines with whole foods as the base, be sure to include foods rich in tryptophan such as turkey, pineapple, tofu, nuts, and chickpeas.
Take a Natural Supplement
Taking a high-quality natural supplement like Tryptochron® can help support healthy serotonin levels in the brain. Tryptochron® provides L-tryptophan, 5-HTP and vitamins B3 (niacin) and B6 (pyridoxine) in a patented formulation to help relieve certain symptoms of serotonin deficiency.
If you feel as if you are not quite yourself lately, it may be a prudent idea to get your serotonin levels checked out. Getting to the root of any possible deficiency will help you to live a healthier and happier life.
 The National Institute of Mental Health
The National Institute of Mental Health  A recent review article
A recent review article In a recent Japanese study, it was found that supplemental vitamin D drops administered to school-aged children reduced their likelihood of developing the flu and other wintertime illnesses. This led the researchers to confirm that the vitamin plays an important role in building up or maintaining the immune system.
In a recent Japanese study, it was found that supplemental vitamin D drops administered to school-aged children reduced their likelihood of developing the flu and other wintertime illnesses. This led the researchers to confirm that the vitamin plays an important role in building up or maintaining the immune system.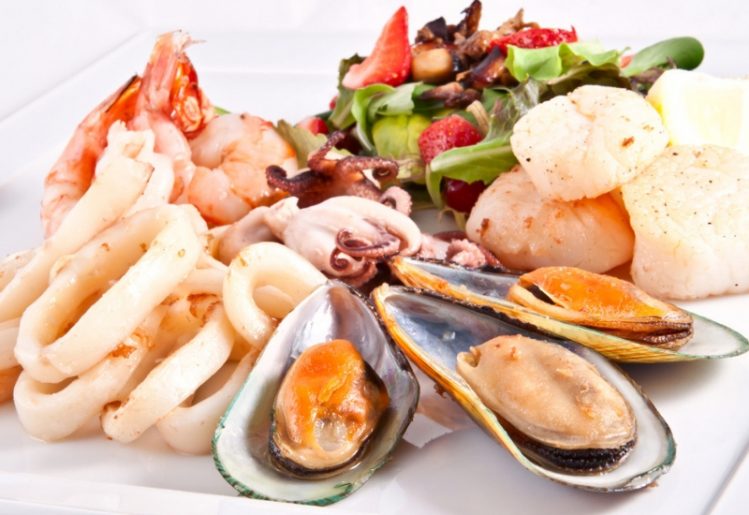 Adding more seafood to your diet is another good way to boost vitamin D levels. In particular, fatty fish, such as tuna, oysters, shrimp, sardines and anchovies, provide higher amounts of the nutrient. Even wild-caught salmon provides a hearty supply of the nutrient.
Adding more seafood to your diet is another good way to boost vitamin D levels. In particular, fatty fish, such as tuna, oysters, shrimp, sardines and anchovies, provide higher amounts of the nutrient. Even wild-caught salmon provides a hearty supply of the nutrient. Accounting for approximately 20 percent of an individual’s body weight
Accounting for approximately 20 percent of an individual’s body weight There are a number of steps that you can take to heal mitochondria or prevent future issues. Like most health issues, getting enough sleep, eating well, engaging in regular exercise and being diligent about reducing stressors in your life will all help to heal these damaged mitochondria.
There are a number of steps that you can take to heal mitochondria or prevent future issues. Like most health issues, getting enough sleep, eating well, engaging in regular exercise and being diligent about reducing stressors in your life will all help to heal these damaged mitochondria. Beginning in 1949, May has been recognized as
Beginning in 1949, May has been recognized as  Another method of keeping in touch with others in your social circle is giving them a call. Phone calls allow for an easier and faster response, so the social interaction has a better flow. This may be the preferred method of communication for those without reliable internet access.
Another method of keeping in touch with others in your social circle is giving them a call. Phone calls allow for an easier and faster response, so the social interaction has a better flow. This may be the preferred method of communication for those without reliable internet access. Depression is always a timely issue to address, particularly because many people do not pay as much attention to their mental well-being as they should. In fact, one person out of every five will suffer from some type of mental illness in his or her lifetime, including depression, anxiety or bi-polar disorder.
Depression is always a timely issue to address, particularly because many people do not pay as much attention to their mental well-being as they should. In fact, one person out of every five will suffer from some type of mental illness in his or her lifetime, including depression, anxiety or bi-polar disorder. Raising the levels of serotonin in the brain is essential for
Raising the levels of serotonin in the brain is essential for